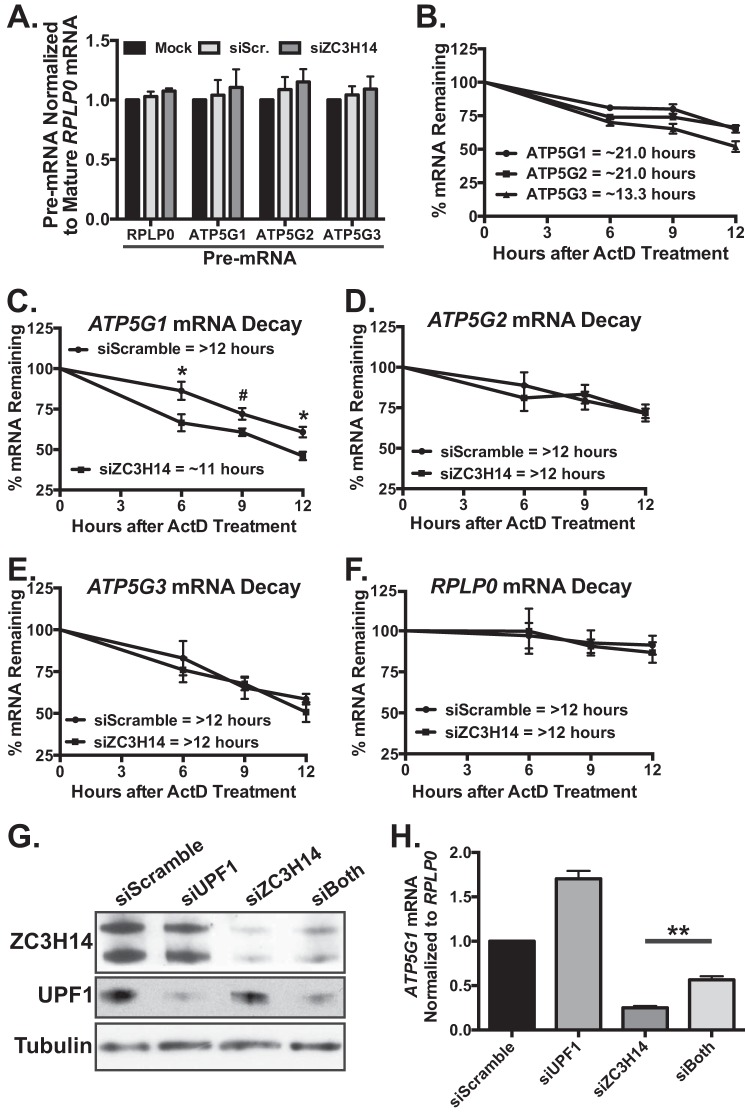
FIGURE 4.
ZC3H14 modulates the decay of ATP5G1 mRNA. A, total RNA isolated from MCF-7 cells treated with mock transfection, Scramble, or ZC3H14 siRNA was used for qRT-PCR analysis with primers that amplify ATP5G1, -2, -3, and RPLP0 pre-mRNAs as well as mature RPLP0 mRNA. Pre-mRNA levels of each transcript are normalized to levels of mature RPLP0 (set to 1.0), and no significant difference was observed in pre-mRNA levels of these transcripts upon ZC3H14 knockdown. B, MCF-7 cells were treated with the transcriptional inhibitor, ActD, and collected at the indicated time points after drug addition. Total RNA isolated from ActD-treated cells was subjected to qRT-PCR analysis with ATP5G1, ATP5G2, ATP5G3, and 18S rRNA (control) primers. mRNA levels were normalized to time 0 and are represented as % of amount present at time 0. The predicted half-lives of ATP5G1 and ATP5G2 were calculated to be ∼21.0 h, although the predicted half-life ATP5G3 was shorter at ∼13.3 h. To examine differences in stability of the ATP5G transcripts upon ZC3H14 knockdown, MCF-7 cells transfected with Scramble or ZC3H14 siRNA were treated with ActD and collected at the indicated time points after drug addition. qRT-PCR analysis of total RNA isolated from these samples with primers specific to ATP5G1, -2, -3, and RPLP0 mRNAs demonstrates a modest but significant decrease in ATP5G1 mRNA stability (C) with no difference in the decay rate of the other transcripts examined (D–F). mRNA levels were normalized to time 0 and are represented as % mRNA remaining. To determine whether ZC3H14 is involved in proper processing of ATP5G1 mRNA, MCF-7 cells were transiently transfected with Scramble, UPF1, ZC3H14, or UPF1/ZC3H14 (siBoth) siRNA. Transfected cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis (G) with ZC3H14, UPF1, and tubulin (control) antibodies and qRT-PCR analysis (H) with primers specific to ATP5G1 and control transcript, RPLP0. Double knockdown of ZC3H14 and UPF1 results in a significant rescue of ATP5G1 mRNA levels compared with ZC3H14 knockdown alone, suggesting that loss of ZC3H14 results in a pre-mRNA processing defect of ATP5G1 upstream of NMD. Data points represent the mean ± S.E. for n = 3 independent experiments. *, **, and # represent p ≤ 0.05, p ≤ 0.01, and p = 0.056, respectively.