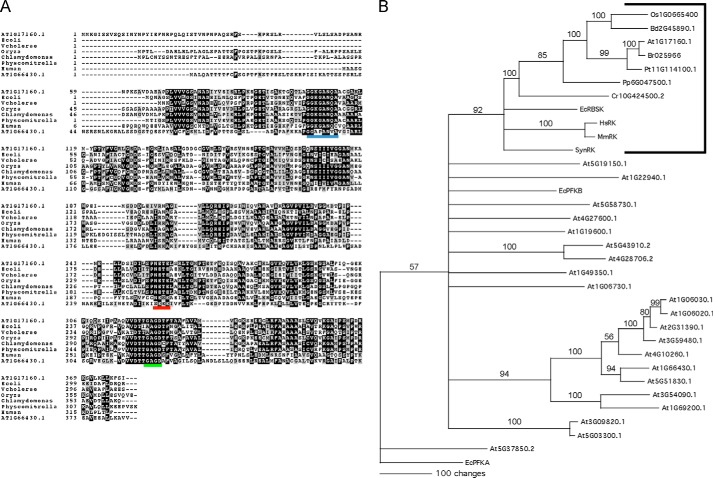
FIGURE 1.
Analyses of At1g17160.1 predict that it is the A. thaliana RBSK. A, alignment of characterized RBSK protein sequences from human and E. coli with predicted RBSKs from the plant lineage indicate that RBSK-like sequences are conserved and share a substrate-specific motif; from rice O. sativa, the moss P. patens, green algal C. reinhardtii, along with a non-RBSK Arabidopsis pfkB protein, At1g66430.1, for comparison. Black and gray boxes indicate amino acids identical or with conservative substitutions in the majority of proteins, respectively. The conserved Gly-Gly (Di-gly) ribose binding motif, the NXXE motif, and the (G/A)XGD motifs are underlined in blue, red, and green, respectively. B, consensus bootstrap tree of 22 Arabidopsis pfkB-type proteins with known RBSKs from A and predicted RBSKs from A with additional predicted RBSKs from B. distachyon, B. rapa, P. trichocarpa, Synechosistis sp. PCC 7509, and mouse (M. musculus). E. coli PFKA was included as an outgroup as it is not related to E. coli PFKB (36). The tree shows the results of 1000 bootstrap replicates of heuristic searches using maximum parsimony using PAUP. Bootstrap values are shown for clades with >50% support and clades with less than 50% support were collapsed.