FIGURE 5.
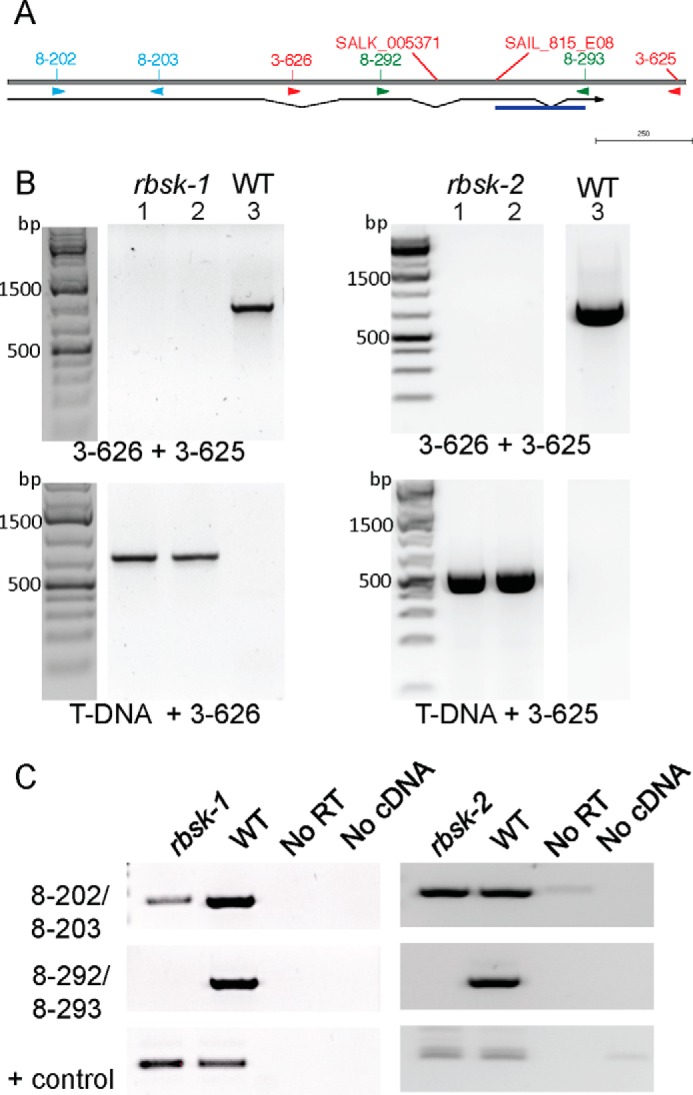
rbsk-1 and rbsk-2 are T-DNA insertional loss of function alleles of AtRBSK. A, schematic of AtRBSK gene architecture with T-DNA insertion positions and primer binding sites shown. Thin horizontal line below indicates position of coding region with introns connecting exons, and arrow indicates direction of open reading frame. DNA sequencing of the T-DNA PCR product revealed a sequence inversion in rbsk-2 (underlined in blue). B, lanes 1 and 2 are PCR products from 2 independent pools of genomic DNA from 4–6 seedlings each, lane 3 is a PCR product from a WT control, using primers flanking the T-DNA insertion sites (top panels) or primers to produce a DNA product spanning the T-DNA-genomic DNA junctions (lower panels) to verify the genotypes of progeny from a homozygous individual for each insertion. Primers used are indicated below their respective ethidium bromide-stained gel image. bp denotes base pairs in molecular weight markers. C, RT-PCR on cDNA from homozygous seedlings or WT (Col ecotype) using primers upstream (top panel) or flanking (middle panel) the T-DNA insertion. Primers specific for an unrelated pfkB family gene, At1g49350, were used as a positive control for the cDNA synthesis and RT-PCR (lower panels). Primer pairs used are indicated. RT, reverse transcriptase; No RT and No cDNA are negative control samples to indicate products from rbsk and WT cDNA are derived from cDNA added, that there is no or low levels of contaminating genomic DNA.
