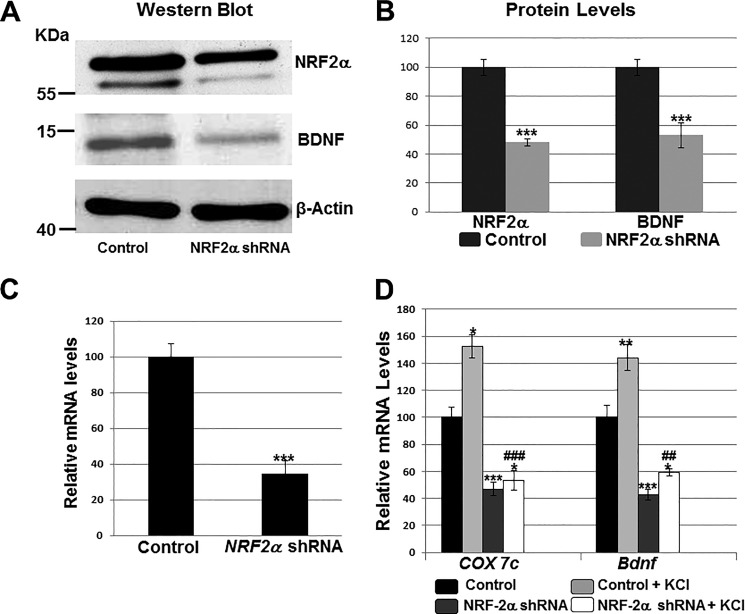
FIGURE 6.
Effect of silencing NRF-2α with shRNA and KCl depolarizing stimulation. Scrambled shRNA vectors served as the control. A and B, Western blots revealed a down-regulation of NRF-2α and BDNF protein levels in shRNA-transfected primary visual cortical neurons. β-Actin served as a loading control (n = 4 for each). The molecular masses of NRF-2α, BDNF, and β-actin are ∼56, ∼14, and ∼42 kDa, respectively. ***, p < 0.001 when compared with controls. C and D, RT-qPCR revealed a down-regulation of NRF-2α, COX7c, and Bdnf transcripts in neurons transfected with NRF-2α shRNA (n = 4 for each) as compared with those transfected with scrambled shRNA controls. ***, p < 0.001 when compared with controls. Primary neurons exposed to KCl up-regulated their mRNA levels for COX7c and Bdnf (n = 4 for each). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 when compared with unstimulated controls. In the presence of NRF-2α shRNA, KCl could no longer up-regulate COX7c and Bdnf transcripts to control + KCl levels (n = 4 for each). ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001 when compared with control + KCl. There were no statistically significant differences in transcript levels of Bdnf and COX7c in neurons treated with NRF-2α shRNA with or without KCl.