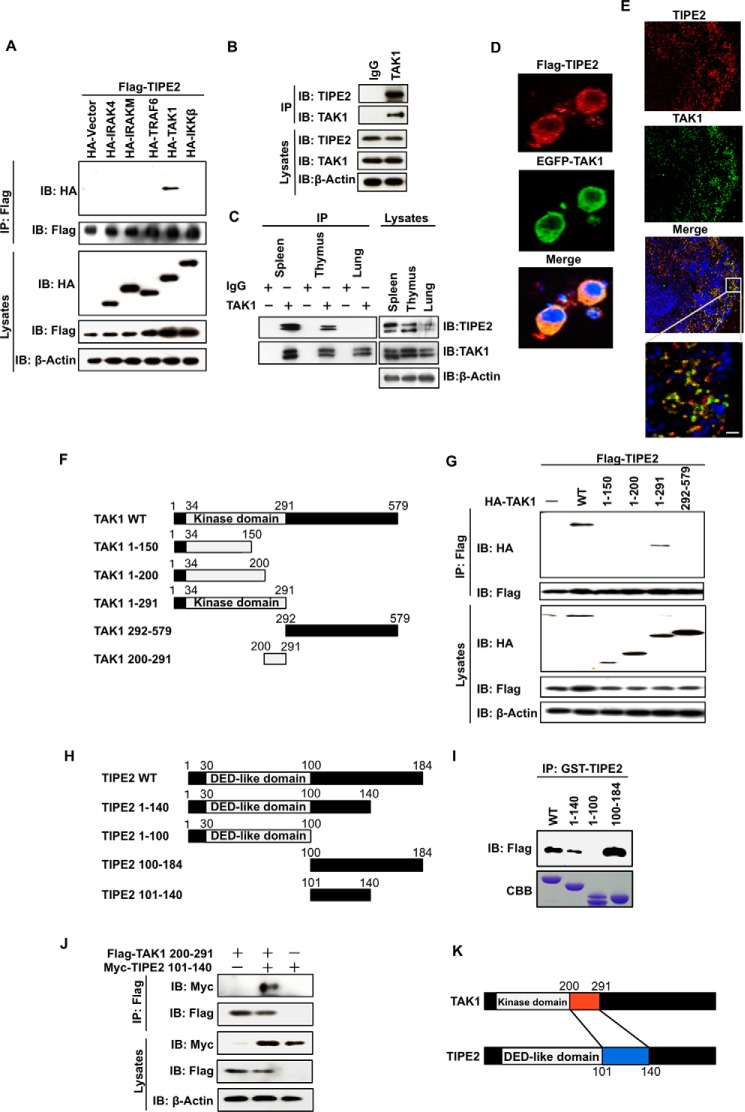
FIGURE 1.
TIPE2 interacts with TAK1 via binding with the TAK1 internal kinase domain. A, HEK293T cells were transfected with FLAG-TIPE2 alone or with both FLAG-TIPE2 and HA-tagged signal molecules, respectively. The cells were extracted 24 h after transfection and immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody. Interactions were detected by Western blotting assay using an anti-HA antibody. The expression of FLAG-TIPE2 and the indicated HA-tagged signal molecules in the immunoprecipitates and whole cell lysates was also detected by Western blotting assay. B, RAW264.7 cells were extracted and immunoprecipitated with control IgG or anti-TAK1 antibody. The presence of TIPE2 or TAK1 in the immunoprecipitates and whole cell lysates was detected by Western blotting assay with anti-TIPE2 antibody or anti-TAK1 antibody. C, mouse spleen, thymus, and lung cell extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with control IgG or anti-TAK1 antibody. The presence of TIPE2 or TAK1 in the immunoprecipitates and whole cell lysates was detected by Western blotting assay with anti-TIPE2 antibody or anti-TAK1 antibody. D, RAW264.7 cells were transfected with FLAG-TIPE2 or EGFP-TAK1 vector. After 24 h, the cells were immunostained with Alexa 594 (red) for FLAG-TIPE2 or with EGFP antibody for EGFP-TAK1. E, the sections of spleen were incubated with anti-TIPE2 and/or with anti-TAK1 antibody for 1 h and then immunostained with Alexa 488 (red) for TIPE2 or Alexa594 (green) for TAK1. The nucleus was stained with TO-PRO-3. Scale bars, 10 μm. F, five truncated mutants of TAK1 (TAK1 1–150, TAK1 1–200, TAK1 1–291, TAK1 292–579, and TAK1 200–291) were generated from the control WT vector. G, HEK293T cells were transfected with FLAG-TIPE2 alone or with both FLAG-TIPE2 and the indicated HA-tagged truncated mutant vectors. After 24 h, the cells were extracted and immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody. Interactions were detected by Western blotting assay using an anti-HA antibody. The expression of FLAG-TIPE2 and the indicated HA-TAK1 deletion mutants in the immunoprecipitates and whole cell lysates was detected by Western blotting assay. H, four truncated mutants of TIPE2 (TIPE2 1–100, TIPE2 1–140, TIPE2 100–184, and TIPE2 101–140) were generated from the control WT vector. I, HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with or without FLAG-TAK1 vector. At 24 h after the transfection, the cells were lysed, and the cell lysates were incubated for 60 min with 0.4 nmol of the indicated GST-TIPE2 protein. The mixture was immunoprecipitated using an anti-GST antibody. The bound proteins were detected by Western blotting assay with anti-FLAG antibody. J, HEK293T cells were transfected with TIPE2 mutant 6× Myc-TIPE2 101–140 alone, FLAG-TAK1 200–291 alone, and a combination of both vectors. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were extracted and immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody. Interactions were detected by Western blotting assay using an anti-Myc antibody. The expression of FLAG-TAK1 and 6× Myc-TIPE2 in the immunoprecipitates and whole cell lysates was detected by Western blotting assay. Interactions were detected by Western blotting assay using an anti-Myc antibody. K, a model for TIPE2 interaction with TAK1 via the TAK1 internal kinase domain. IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation; CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue.