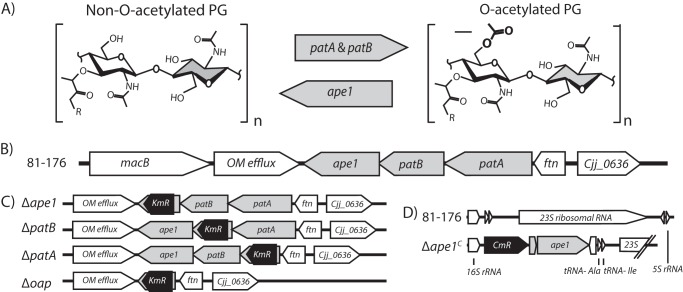
FIGURE 1.
Location of O-acetyl groups on peptidoglycan subunits, organization of the C. jejuni OAP gene cluster, and description of deletion mutant and complement construction. A, structures of the disaccharide muropeptides showing non-O-acetylated PG and O-acetylated PG, location of O-acetylation (arrow), and the putative involvement of the oap genes. B, genomic organization of the C. jejuni OAP gene cluster in the 81-176 wild-type strain (gray). cjj81176_0638, cjj81176_0639, and cjj81176_0640 are the C. jejuni homologs of Δape1, ΔpatB, and ΔpatA respectively, as identified by BLAST using the N. gonorrhoeae OAP genes sequences. C, OAP mutants were generated by homologous recombination with a mutated copy of the gene (or the entire cluster for Δoap) in which a portion of the gene (or cluster) was deleted and replaced with a non-polar KmR cassette (aphA3) (47). Resistance to Km was used as a selective marker for successful homologous recombination in C. jejuni with the mutated gene. D, complement construction (with Δape1 used as an example, designated Δape1C). Each OAP gene plus upstream sequence containing the ribosomal binding site was cloned into the pRRC vector that contains homologous regions to three ribosomal intergenic regions downstream of the CmR cassette for selection of successful C. jejuni transformants. Complement constructs were transformed into their respective mutant backgrounds. MacB, macrolide-specific efflux pump; OM efflux, outer membrane efflux; ftn, ferritin; 23S, 23S ribosomal RNA (48).