FIGURE 7.
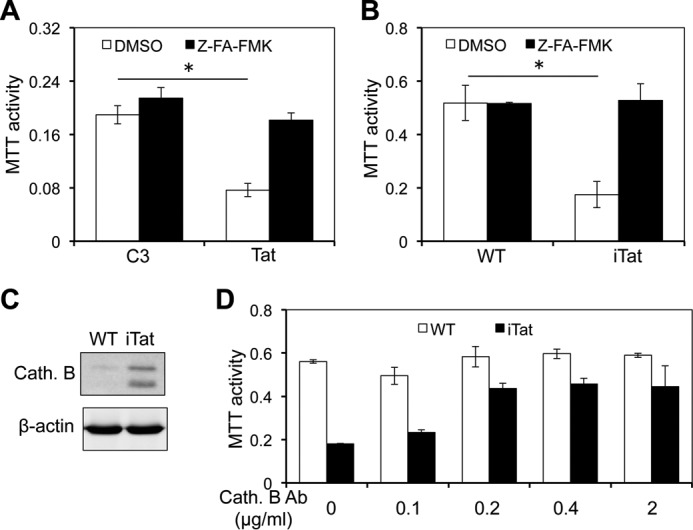
Cathepsin B inhibitor inhibited the neurotoxicity of the supernatants of Tat-expressing astrocytes. A, human primary fetal astrocytes were transfected with pcDNA3 (C3) or Tat, cultured for 72 h, and then treated with cathepsin B inhibitor Z-FA-fmk (100 μm) for 24 h. DMSO, the solvent of Z-FA-fmk, was included as a control. The supernatants were collected and used to determine the neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y using the MTT assay. B–D, primary astrocytes were isolated from WT and iTat mice and cultured in the presence of Dox for 3 days and treated with cathepsin B inhibitor Z-FA-fmk as above. The supernatants were evaluated for their neurotoxicity as above (B). The cells were harvested for cell lysates. The cathepsin B (Cath. B) in both supernatants and cell lysates was determined by Western blotting (C). In addition, the supernatants were incubated with different concentrations of an anti-cathepsin B antibody (Cath. B) for 1 h and assayed for their neurotoxicity as above (D). Error bars, S.D.; *, p < 0.05.
