Figure 1. Alternative strategies to triage women with ASC-US or LSIL, and high-risk HPV-positive on index screen.
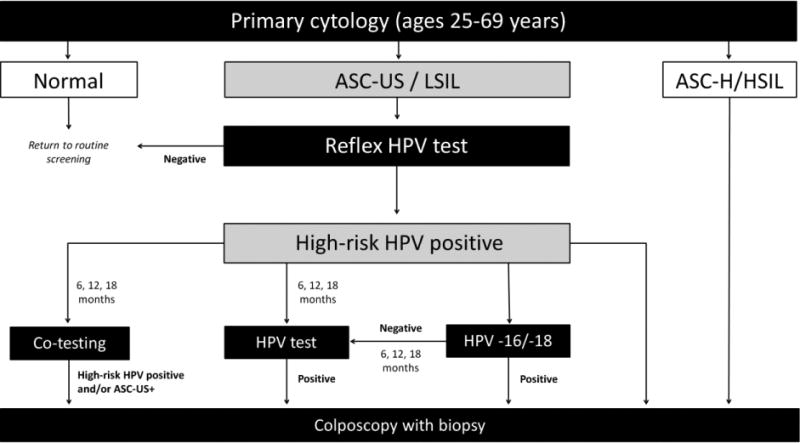
ASC-US+: atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance or worse, ASC-H: atypical squamous cells, cannot rule out high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, HPV: human papillomavirus, HSIL: high-grade intraepithelial lesion.
Flow diagram representing alternative screening strategies. This analysis focused on the follow-up of women with ASC-US/LSIL on their primary cytology screen, with a positive HPV result using reflex HPV DNA testing. We compared four main alternative strategies for screening triage; co-testing (i.e., HPV DNA testing and cytology in combination), HPV testing (i.e., HPV DNA testing to detect high-risk HPV), HPV -16/-18 genotyping (i.e., only referring HPV-16/-18 positives to colposcopy and requiring a persistent HPV positive result at 6, 12, or 18 months for women positive for other high-risk HPV types), or direct colposcopy for all HPV positive women. We varied the wait-time between index result and triage procedure by 6, 12 and 18 months for strategies other than direct colposcopy. Women negative for high-risk HPV could return to a routine screening schedule.
