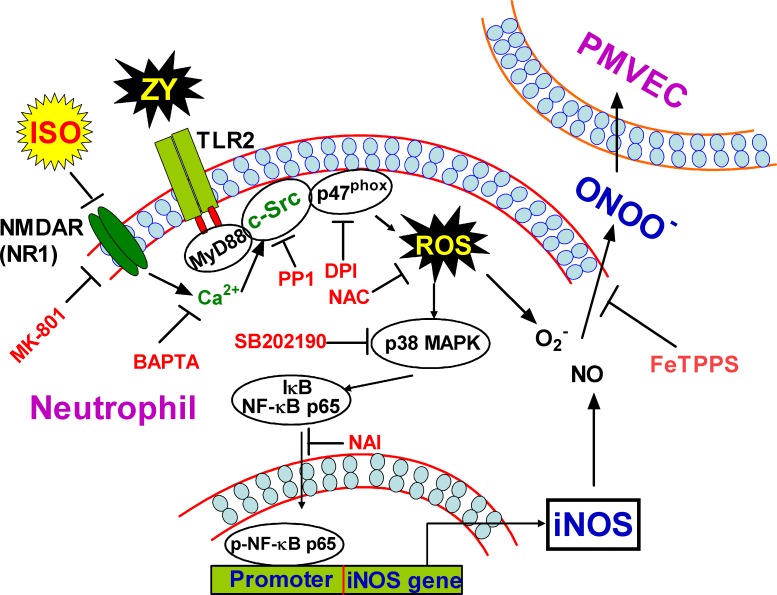
Figure 8. Schematic diagram of the proposed signaling pathways elicited by zymosan but inhibited by subanesthetic isoflurane.
Zymosan induces ROS production through a TLR2/MyD88/c-Src/NADPH oxidase pathway, which in turn caused the activation of p38 MAPK and consequently the activation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB. NF-κB thus switches on iNOS expression, and increases NO production and ONOO− release from neutrophils, which eventually permeabilizes adjacent PMVECs. Subanesthetic isoflurane exerts a protective role for this pathological process by inhibiting c-Src activity, which is probably attributed to isoflurane targeting of the NMDA glutamate receptor and thereby suppression of the calcium signaling in neutrophils.