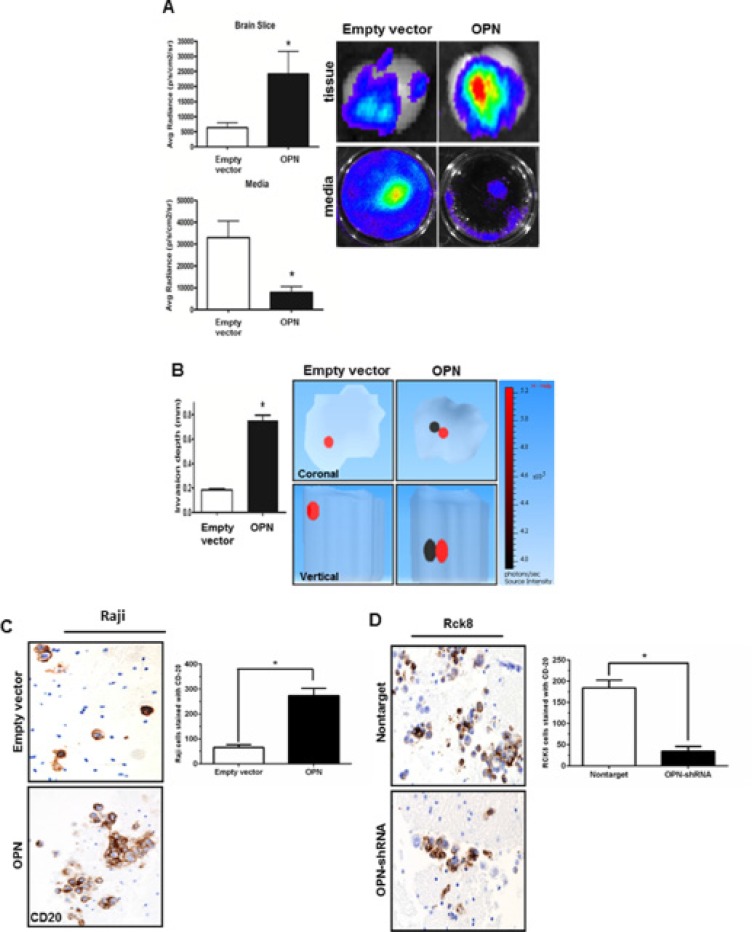
Figure 2. Osteopontin significantly increases the brain tissue invasiveness of B lymphoma cells.
The impact of OPN on invasiveness of B lymphoma cells in the brain tissue is studied by ex vivo murine brain slice invasion assay. Rck8-OPN shRNA and Raji-OPN cells were compared to their respective controls. (A) Bioluminescence imaging is used to analyze the invasion of luciferase-transfected Raji-OPN cells into murine brain slices compared to their respective control cells. OPN is shown to significantly promote the invasion of lymphoma cells into the brain slices. (B) Tomographic analysis is performed to analyze the invasion depth of the luciferase-transfected Raji-OPN B lymphoma cells into the murine brain slices compared to their controls. OPN is shown to significantly increase the depth of invasion. The dark circle indicates the most concentrated area of tumor cells and the red circle indicates the least concentrated area of tumor cells. The scale bar indicates the source intensity. (C and D) CD20 immunohistochemistry (IHC) is performed to identify the number of Raji-OPN and Rck8-OPN shRNA invading the brain slices compared to controls. OPN is shown to increase the number of B lymphoma cells invading the brain slices. (Error bars in the figures show SEM of triplicates. *P < 0.001).