Figure 1. Radiation-resistant HL60/RX cells and adriamycin-resistant HL60/ADR cells show an increased radioresistance and increased activity of the Hedgehog pathway than HL60 cells.
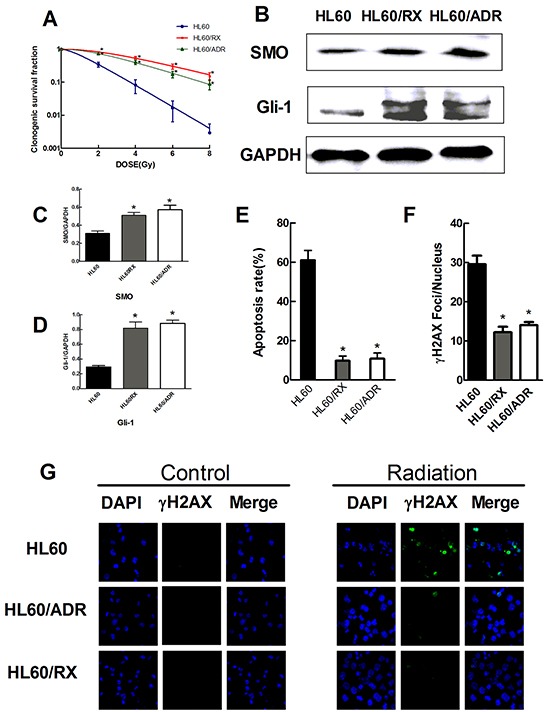
A. Survival curves of HL60, HL60/ADR, and HL60/RX cells after radiation. HL60/ADR and HL60/RX cells show great resistance to radiation than the parental cells. B–D. The protein expression of SMO and Gli-1 in HL60, HL60/ADR, and HL60/RX cells. GAPDH was used as loading control. E. The percentage of apoptosis cells in HL60, HL60/ADR, and HL60/RX cells after radiation (4.8Gy). F. Average number of γ-H2AX foci/nucleus after radiation (4.8Gy). G. γ-H2AX formed in the nucleus was more significant in HL60 cells compared with HL60/ADR and HL60/RX cells. *, p<0.001 vs HL60.
