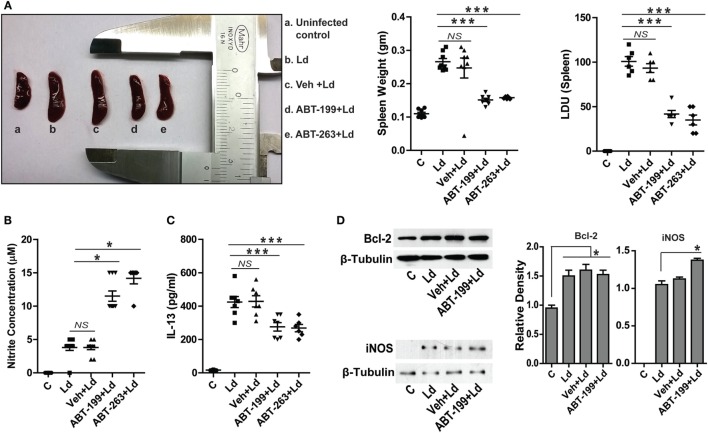
Figure 6.
ABT-199 treatment reduces parasite burden in mice. (A) L. donovani infection-induced splenomegaly in mice (b) which shows significant reduction in ABT-199 (d) and ABT-263 (e) treated group. Scatter plots show spleen weight and splenic parasite burden in terms of Donovan units. Note the reduction in total splenic weight as well as parasite burden in ABT-199- and ABT-263-treated group. LDU, Leishman Donovan units; Ld, Leishmania donovani; Veh, vehicle (DMSO). (B) Griess’ assay shows a significant increase in the serum nitrite levels in ABT-199 as well as ABT-263 treated mice as compared to only infection or vehicle treated controls, with negligible concentrations of serum nitrite. (C) IL-13 ELISA shows elevated levels of IL-13 cytokine in the serum of mice infected with L. donovani. Note that ABT-199- and ABT-263-treated mice show lower levels of IL-13. Vehicle controls show IL-13 levels comparable to only infection group. Data in (A–C) are mean ± SEM (n = 6–8); *P ≤ 0.05, ***P < 0.001; Mann–Whitney test. (D) Western blots from crude splenic lysates show increased Bcl-2 expression in all infected groups. ABT-199 treatment had no effect on the Bcl-2 expression. On the other hand ABT-199-treated group showed increased iNOS expression. Adjacent bar graphs show the densitometric plots for the Bcl-2 and iNOS blots respectively. Ld, Leishmania donovani; Veh, vehicle (DMSO). *P ≤ 0.05; Mann–Whitney test.