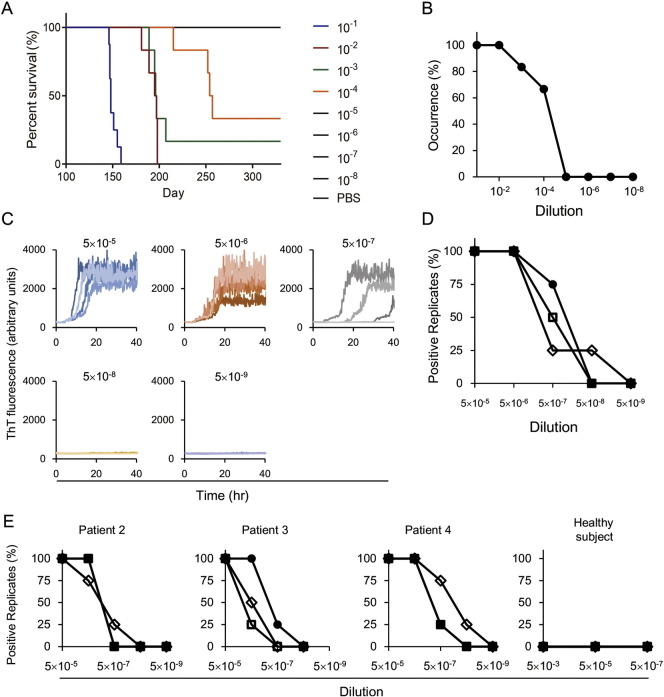
Fig. 1.
Analysis of brain tissues from patients with sporadic CJD using bioassay and endpoint RT-QuIC assay. (A, B) Transmission of human prions to Ki-ChM mice. (A) Survival curve for Ki-ChM mice inoculated with a serially diluted brain homogenate from Patient #1. (B) Endpoint titration of brain tissue from a sCJD patient (Patient #1) using the bioassay. Each value represents the percentage of occurrence of symptoms caused by prion disease. (C, D) Endpoint RT-QuIC assay of brain tissue from Patient #1. (C) Brain tissue was diluted and the endpoint RT-QuIC assay was used to evaluate prion-seeding activity. (D) Each value represents the percentage of positive reactions for each dilution rate. The experiments were performed in triplicate for each sample. (E) Endpoint RT-QuIC assay of brain tissues from patients with sCJD (Patients #2–4). The experiments were performed in triplicate for each sample.