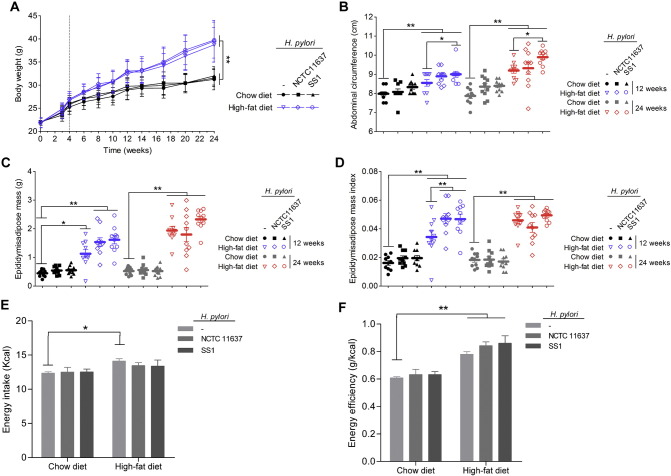
Fig. 1.
Effects of H. pylori infection and different dietary regiments on body composition. Mice were fed either a chow or a high-fat diet (HFD) for 12 weeks and 24 weeks. H. pylori-infected groups were intragastrically administered either SS1 strain or NCTC11637 strain with a 2 day interval for a total of five infusions. Chow and HFD fed control groups were gavaged with vehicle (Brucella broth). (A) Body weight curves; (B) abdominal circumference; (C) epididymisadipose mass; (D) epididymisadipose mass index (ratio between epididymisadipose mass and body weight); (E) energy intake; (F) energy efficiency (ratio between body weight gain and energy intake). The body weight was significantly increased by four weeks after HFD. n = 8–10. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.