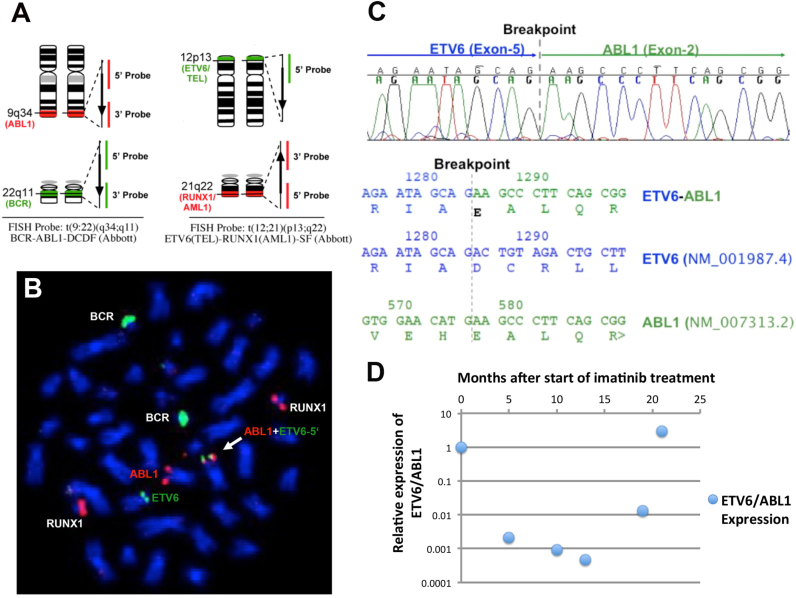
Fig. 1.
Detection of the ETV6-ABL1 fusion: A. Schematic diagram of commercial BCR-ABL1-DCDF and the RUNX1-ETV6-ES FISH probe designs. B. Co-hybridization of the BCR-ABL1-DCDF and the RUNX1-ETV6-ES FISH probes on the metaphase chromosomes preparation from the patient sample: RUNX1 and BCR locus were intact. As predicted, one of the green signals for ETV6-5′ region was observed co-localized with one of the ABL1 loci on chromosome 9 (white arrow). C. Electropherogram of the sequence spanning the breakpoint confirming an in-frame fusion between ETV6 exon 5 and ABL1 exon2. (upper panel) and fusion transcript sequence and the corresponding wild type sequences including the amino acid sequence (lower panel). The vertical grey line indicates the position of the breakpoint. D. Overview of the ETV6-ABL1 fusion transcript level during the course of treatment with reference to that at the diagnosis. Imatinib treatment was started 2 months after the diagnosis time point. MRD: minimal residual disease: * Relative Expression of ETV6/ABL1: The expression level of ETV6/ABL1 at the time of diagnosis is set to 1. ETV6-ABL1 expression levels are normalized to the expression levels of ABL1. Relative Expression=2exp(Δ CtETV6/ABL1(follow-up)-Δ CtETV6/ABL1 (diagnosis)).