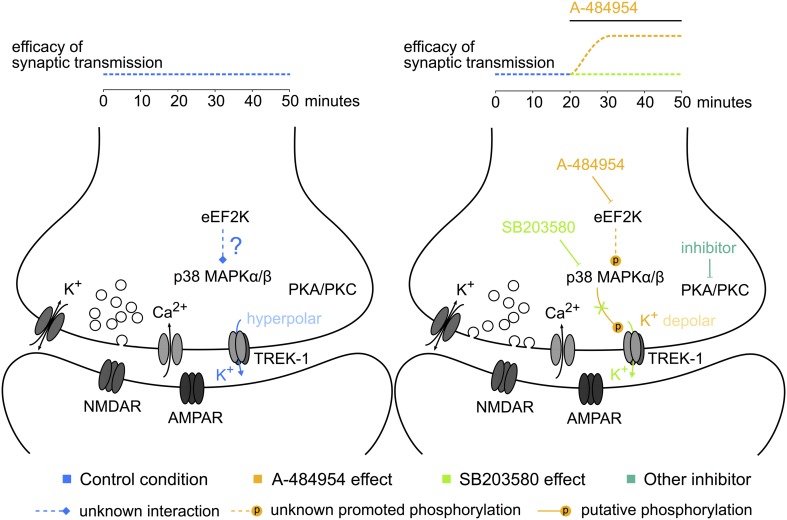
FIGURE 12.
Potential elements of the eEF2K-inhibition mediated potentiation. The sketch to the left indicates some of the components studied and their interaction or activity during baseline stimulation. To the right, the modulation of the phosphorylation level and the resulting synaptic potentiation after eEF2K-inhibition are presented. The color of the text corresponds to the potentiation indicated above the sketch. Dotted lines: unknown pathways of interaction; lines ending with a stroke: inhibition; lines ending with a P: phosphorylation. A hypothesis based on our data implicates that the inhibition of eEF2K mediates a potentiation of synaptic transmission by altering the release probability of vesicles with the participation of p38 MAPK and potassium channel phosphorylation-mediated reduction of the resting membrane potential at the synaptic button.