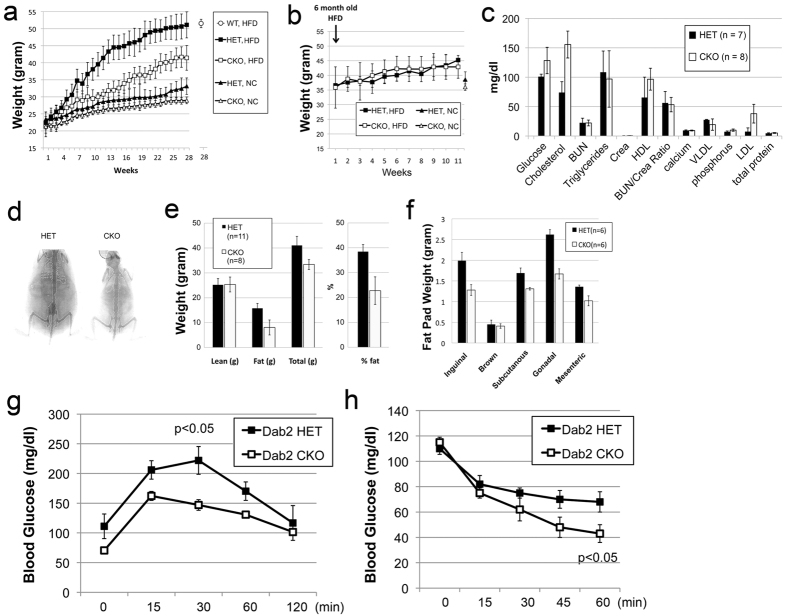
Figure 1. Resistance to high fat diet-induced weight gain in Dab2 conditional knockout mice.
(a) Wild-type (WT), Dab2 Sox2-Cre conditional knockout (CKO), and heterozygous (HET) controls male mice at 7 weeks of age were placed on either normal chow (NC) or high fat diet (HFD) for additional 28 weeks. The averages of weight from 10 to 11 animals are shown with standard deviations. The weight for the WT group (n = 7) on HFD is shown for only the last time point. (b) Impacts of HFD on weight gain in mature mice were examined. The mice were initially fed a NC and then switched to a HFD at 6 months of age for another 11 weeks, in comparison to mice that were continued on NC (only the last time point is shown). No statistical difference was found between the two genotypes. (c) Blood chemistry analysis was performed on fasting dab2 CKO and HET mice that had been fed with a HFD. The items are shown as mg/dL, except total protein that is shown as g/dL. BUN, Blood Urea Nitrogen; Crea, creatinine; LDL, low density lipoprotein; VLDL, very low density lipoprotein; HDL, high density lipoprotein. (d) Representative PIXI images are shown of 6-month-old dab2 CKO and HET littermates fed a HFD. (e) The lean, fat, and total body masses were determined by the DEXA system and the means and standard deviations from a group of 11 HET and 8 CKO mice are presented. The difference in the percentage of body fat is statistically significant (p < 0.005) between dab2 CKO and HET. (f) The fat tissue masses (inguinal, brown, subcutaneous, gonadal, and mesenteric) were determined in 6 each of the dab2 HET and CKO male mice (p < 0.01, except brown fat). (g) Glucose tolerance test: Mice (6 each) were fasted for four hours and injected intraperitoneally (IP) with glucose (20% in saline) at a dosage of 2 g of glucose/kg body mass. A drop of blood (about 5 μl) was collected from tail bleeding at each time point for analysis by glucose meter. (h) Insulin sensitivity test: Mice (6 per group) were fasted for four hours, and then injected (IP) with insulin at a dosage of 0.6 u/kg body weight.