Figure 2.
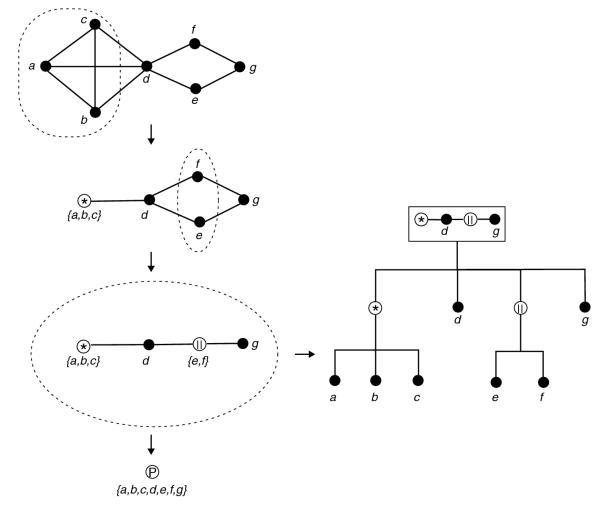
Modular decomposition of the example graph in Figure 1. Modular decomposition gives a labeled tree that represents iterations of particular quotients, here the successive quotients on the modules {a,b,c} and {e,f}. Series are labeled by an asterisk within a circle, parallel by two parallel lines within a circle, and prime by a P within a circle. The prime is advantageously labeled by its structure. The graph can be retrieved from the tree on the right by recursively expanding the modules using the information in the labels. Therefore, the labeled tree can be seen as an exact alternative representation of the graph.
