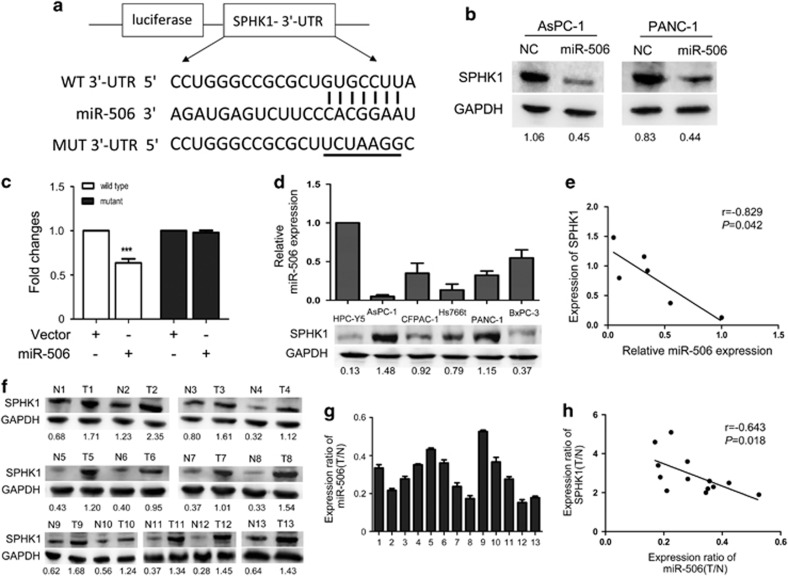
Figure 4.
miR-506 targets SPHK1. (a) The predicted miR-506-binding sequence in the 3′-UTR of SPHK1 mRNA is shown. Mutations were generated in the SPHK1 3′-UTR sequence at the complementary sites for the seed regions in miR-506. (b) Western blot analysis of SPHK1 expression in AsPC-1 and PANC-1 cells transfected with NC or miR-506 mimic after 48 h; GAPDH was used as a loading control. (c) Analysis of luciferase activity. 293 T cells were transfected with pGL3-wild-SPHK1 3′-UTR or pGL3-mutant-SPHK1 3′-UTR using a vector control or miR-506. The Renilla luciferase vector was used as an internal control. *P<0.05. (d) miR-506 and SPHK1 expression in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Top: qRT–PCR analysis of miR-506 levels; bottom: western blot analysis of SPHK1 protein levels. (e) An inverse relationship between miR-506 and SPHK1 protein levels was shown in the pancreatic cancer cell lines and in the immortalized pancreatic cell line HPC-Y5 based on Spearman's correlation. (f) Western blot analysis of SPHK1 in 13 pairs of pancreatic cancer tissues. (g) The related expression levels of miR-506 in the 13 pairs of tissue are indicated. (h) An inverse relationship between miR-506 and SPHK1 protein was demonstrated in pancreatic cancer tissues based on Spearman's correlation.