Fig. 6.
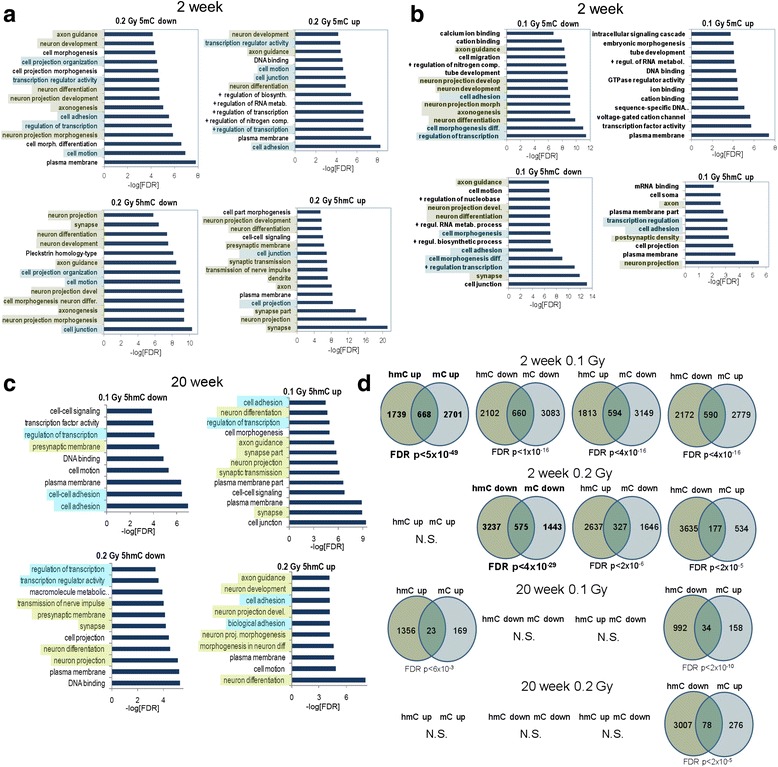
a Gene ontology analysis for the 0.1 Gy 56Fe dose at the 2-week time point. Regions with decreased 5mC were associated with pathways in neuronal categories linked to axon guidance, axogenesis, neuronal development and differentiation. There was an overlap in non-neuronal categories 56Fe ion irradiation with that seen 22 weeks following proton irradiation. Regions with both decreased and increased 5hmC had highly significant overlap with pathways linked to decreased 5mC. Green highlights neuronal categories and blue highlights non-neuronal categories also observed 22 weeks following proton irradiation. b Gene ontology analysis for the 0.2 Gy 56Fe dose at the 2-week time point. Regions with decreased and increased 5mC were associated with pathways in neuronal categories linked to axon guidance, axogenesis, neuronal development and differentiation. Regions with decreased 5hmC were associated with neuron projection, synapse, neuron differentiation, axon guidance, and axonogenesis. Regions with increased 5hmC were associated with neuron projection development, neuron projection and differentiation, presynaptic membrane, synaptic transmission and synapse, dendrite, axon. c Gene ontology analysis at the 20-week time point. Comparing 0.1 and 0.2 Gy, there is an overlap in neuronal categories between regions with upregulated 5hmC (green). Blue highlighted categories are non-neuronal categories that were also observed for the 20-week time point following proton irradiation. The significance of pathways was lower at the 20-week than the 2-week time point. There were no significant gene categories at an FDR < 0.0001 for 5mC. d Venn diagrams depict the overlap between significant 5hmC and 5mC DMRs (q < 0.01, difference > 50 tags, 5 kb window) at the indicated doses and indicated time points. a At the 2-week time point and 0.1 Gy, regions with both decreased and increased 5hmC had highly significant overlap with pathways linked to decreased 5mC. In addition, regions with increase 5hmC had highly significant overlap with pathways linked to increased 5 mC. b At the 2-week time point and 0.2 Gy, regions with increased 5hmC had highly significant overlap with pathways linked to decreased 5mC, while regions with decreased 5hmC had highly significant overlap with pathways linked to increased 5mC. c At the 20-week time point at 0.1 Gy, regions with decreased 5hmC had highly significant overlap with pathways linked to increased 5mC and regions with increased 5hmC and significant overlap with pathways linked to regions to increased 5mC. d At the 20-week time point at 0.2 Gy, regions with decreased 5hmC only had highly significant overlap with pathways linked to increased 5mC
