FIGURE 3.
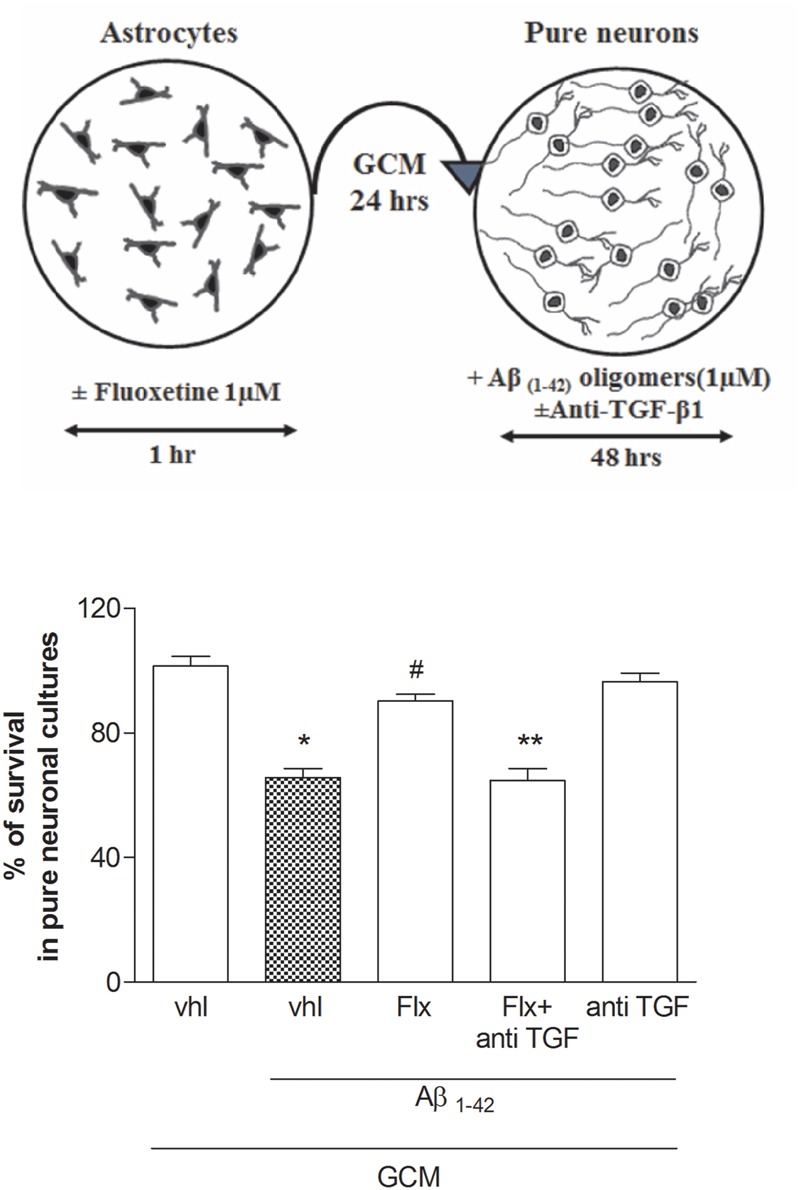
Fluoxetine prevents Aβ toxicity via a paracrine mechanism mediated by TGF-β1. Pure cultures of rat cortical neurons were exposed to glial conditioned medium (GCM) collected from cortical astrocytes 24 h after a transient (1 hr) exposure to1 μM fluoxetine or vehicle. Neurons were then treated with Aβ1-42 oligomers (1 μM) for 48 h in the presence or absence of anti-TGF-β1 antibody. A schematic drawing of this experimental protocol is shown in the upper panel. Anti-TGF-β1 was added at a concentration of 2 μg/ml just before transferring of GCM into pure neuronal cultures. Aβ toxicity in pure neuronal cultures was assessed by MTT assay and is expressed as percentage of neuronal survival. Values are means ± SEM of 12–15 determinations ∗p < 0.05 vs. control (GCM, vhl); #p < 0.05 vs. Aβ1-42 alone (GCM, Aβ1-42, vhl); ∗∗p < 0.05 vs. Aβ1-42 and fluoxetine (GCM, Aβ1-42, Flx) (One-way ANOVA + Bonferroni’s test).
