Fig. 2.
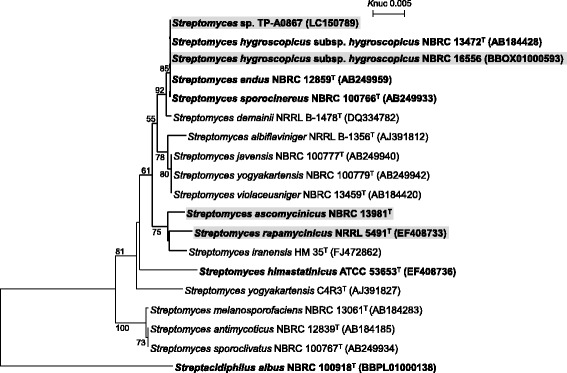
Phylogenetic tree of Streptomyces strains based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. The 16S rRNA sequences were obtained from GenBank, whose accession numbers are shown in parentheses, whereas that of Streptomyces ascomycinicus NBRC 13981T was downloaded from ‘Sequence Information’ of the NBRC Culture Catalog Search (www.nbrc.nite.go.jp/NBRC2/SequencSearchServlet?ID=NBRC&CAT=00013981&DNA=2). The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method [45] using sequences aligned by ClustalX2 [9]. All positions containing gaps were eliminated. The building of the tree also involves a bootstrapping process repeated 1,000 times to generate a majority consensus tree, and only bootstrap values above 50 % are shown at branching points. Streptacidiphilus albus NBRC 100918T was used as an outgroup. Strains whose genome were sequenced are boldfaced. Among the genome-sequenced strains, those harboring the putative alchivemycin biosynthetic gene cluster are shadowed in gray
