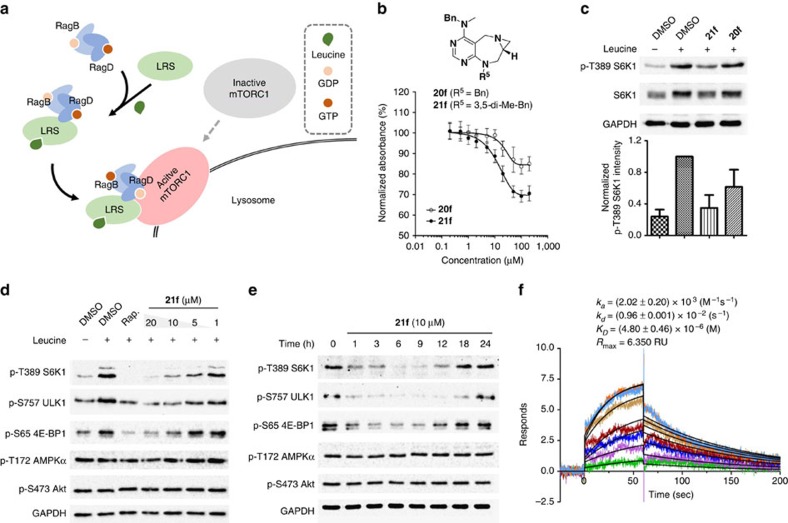
Figure 5. Discovery of chemical modulator for LRS–RagD interaction.
(a) Noncanonical role of LRS. Leucine-loaded LRS binds to RagD, which promotes the translocation of mTORC1 to lysosomal surface and subsequent activation. (b) Dose–response curves in ELISA of 20f and 21f. The results represent the mean of three biological replicates; error bars represent the s.e.m. (c) Effects of 20f and 21f on mTORC1 signalling pathway. HEK293T cells were treated with 20 μM of 20f and 21f for 3 h. As a negative control, cells were deprived of leucine for 3 h. Level of phospho-T389 S6K1 were quantified against a DMSO control. The bar graph represents the mean of five biological replicates; error bars represent the s.e.m. (d) Dose-dependent effects of 21f to mTORC1 signalling pathway. HEK293T cells were treated with 20, 10, 5 and 1 μM of 21f for 3 h. As a negative control, cells were deprived of leucine for 3 h. Rapamycin (Rap) was used as a positive control and cells were treated with 200 nM of Rap for 3 h. (e) Time-course study of the inhibitory effect of 21f on mTORC1 signalling pathway for 0–24 h. HEK293T cells were treated with 10 μM of 21f. Phospho-T389 S6K1, phospho-S757 ULK1, phospho-S65 4E-BP1, phospho-T172 AMPKα, phospho-S473 Akt, S6K1 and GAPDH were determined by western blot. The western blot results shown are representative of three biological replicates. (f) Sensorgrams of SPR spectroscopy of 21f showed its concentration-dependent binding to purified LRS. The concentration plotted are 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 12.5, 15, 17.5 and 20 μM, in order of increasing 21f. The curve fittings are shown in black. The sensorgrams represent the mean of two biological replicates. The full gel images of western blotting are in Supplementary Fig. 22.