Figure 3.
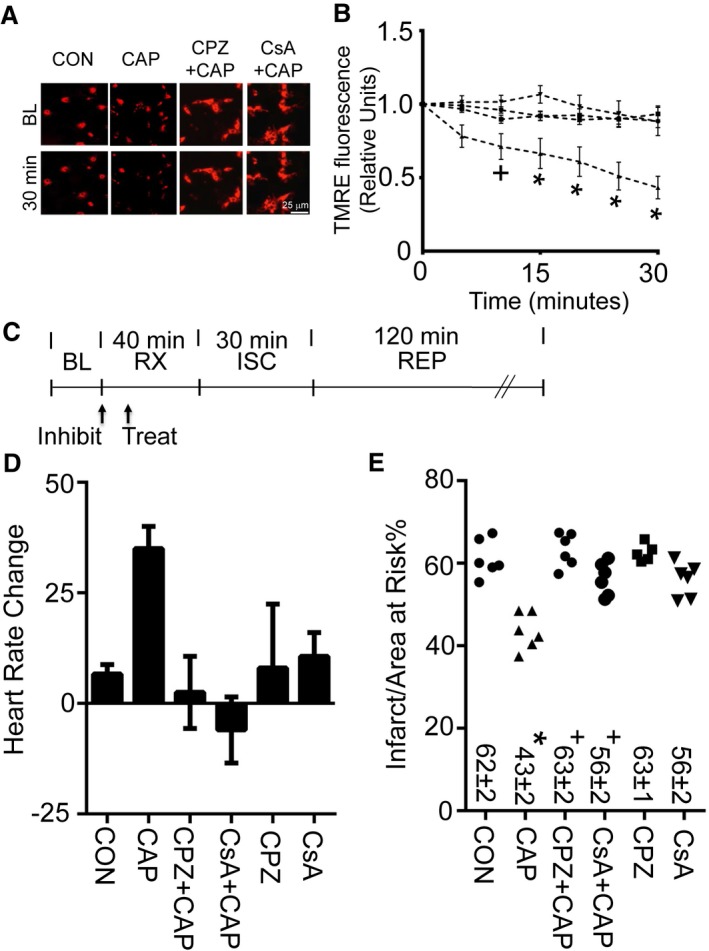
Calcineurin inhibition regulates mitochondrial membrane potential and infarct size. A, Representative images (at BL and 30 minutes after drug application) for assessment of mitochondrial membrane potential by TMRE for primary neonatal cardiomyocytes treated with CON (dimethyl sulfoxide) or CAP (1 μmol/L). A subset of groups was treated 10 minutes prior to CAP with CPZ (1 μmol/L) or CsA (1 μmol/L). B, TMRE fluorescence measurements for CON, CAP, CPZ plus CAP, or CsA plus CAP for 30 minutes, as assessed by TMRE (n=3 biological replicates per group, + P<0.05 or *P<0.01 for CON, CPZ plus CAP, or CsA plus CAP vs CAP). C, Experimental protocol for myocardial ISC–REP studies. “Treat” indicates time of treatment for either CON or CAP given 30 minutes prior to ISC. Arrow with “Inhibit” indicates time of treatment for either CPZ (3 mg/kg) or CsA (2.5 mg/kg) 40 minutes prior to ISC. D, Heart rate increase caused by CAP is blocked by either CPZ or CsA. E, Either CPZ or CsA blocks CAP‐induced infarct size reduction. For comparison purposes, both CON and CAP were replotted from Figure 2D and 2E for panels (D) and (E), respectively. *P<0.01 vs CON, + P<0.01 vs CAP alone. BL indicates baseline; CAP, capsaicin; CON, control; CPZ, capsazepine (3 mg/kg); CsA, cyclosporine (2.5 mg/kg); ISC, ischemia; REP, reperfusion; RX, treatment; TMRE, tetramethylrhodamine, ethyl ester.
