Figure 1.
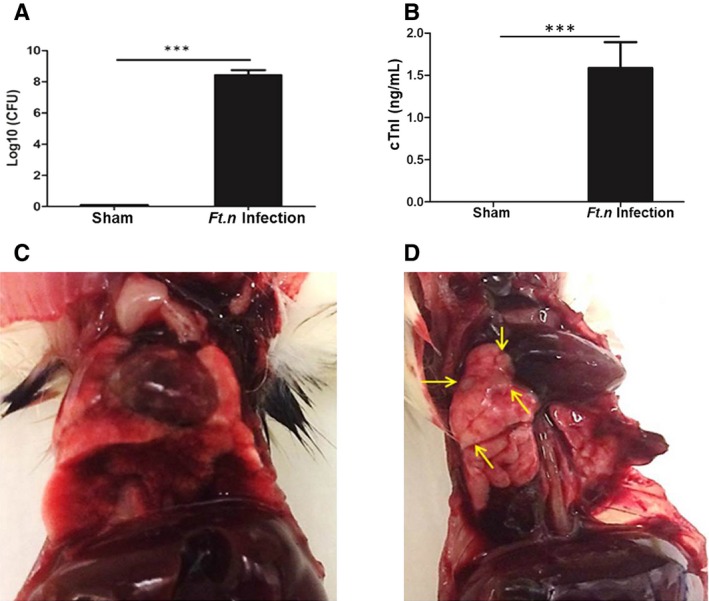
Ft.n bacterial load correlates with cardiac damage. Wild‐type BALB/C mice were infected with Ft.n (25 CFUs) through the intranasal route, and after 96 hours of incubation, mice were euthanized and lungs and blood were retrieved for further analysis. (A) Bacterial burden was determined by CFU assay by serial dilution and plating of the whole‐lung homogenates on chocolate blood agar plates (2 independent experiments; N=6). (B) Serum cardiac troponin‐I (cTnI) levels were determined by an ELISA assay kit (***P<0.0005; 2 independent experiments; N=6). Images shown in (C) and (D) are lungs and hearts of sham‐treated and Ft.n‐infected mice. Yellow arrows indicate bacterial colonization (lesions) in lungs of infected animals, a representative image from 3 independent experiments (N=12). CFU(s) indicates colony forming unit(s); ELISA, enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay.
