Figure 3.
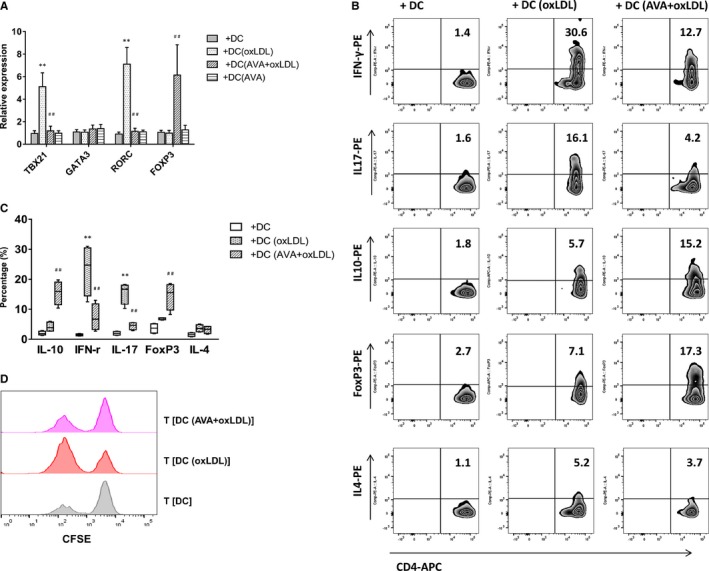
Th1 and Th17 polarization induced by oxidized low‐density lipoprotein (oxLDL)‐treated dendritic cells (DCs) were inhibited, while T regulatory cells were induced by atorvastatin. A, T‐cell polarization‐related transcription factors. Quantitative PCR data represent mean±SD of 6 independent experiments. B, Intracellular staining of cytokine production in T cells. Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured with oxLDL‐ or atorvastatin (AVA)+oxLDL–treated autologous DCs for 13 days. After stimulation, T cells were activated with anti‐CD3 monoclonal antibody and intracellular staining of cytokine production. Percentages of interferon‐γ (IFN‐γ)‐, interleukin (IL)‐17‐, IL‐10‐producing cells, and FoxP3‐positive cells in T (DC), T (DC [oxLDL]), or T (DC [AVA+oxLDL]) cells are presented. Figure depicts a representative experiment of 5. C, Frequency of T‐cell subsets is summarized. Results show mean±SD (n=5). D, T (DC [AVA+oxLDL]) cells suppressed primary T‐cell proliferation. T‐cell proliferation was measured by CFSE staining. Naïve CD4+ T cells were stimulated with mature DCs alone or in the presence of T (DC), T (DC [oxLDL]), or T (DC [AVA+oxLDL]) cells at a 1:1 ratio. Results show a representative experiment of 4. **P<0.01, T (DC [oxLDL]) vs T (DC); ## P<0.01, T (DC [AVA+oxLDL]) vs T (DC [oxLDL]). CFSE indicates carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
