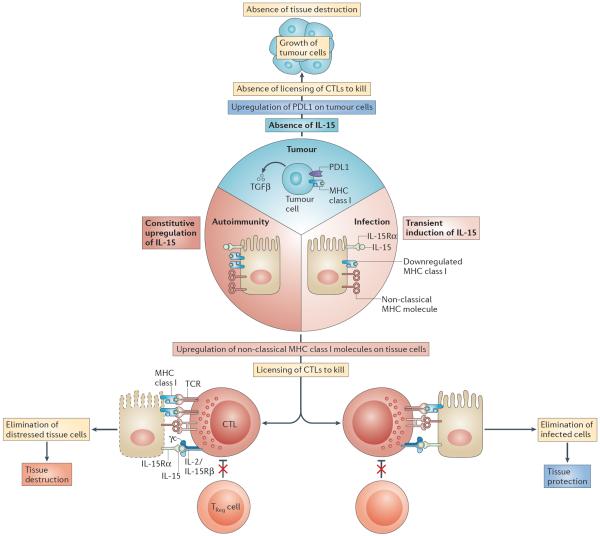
Figure 4. Proposed roles of IL-15 in tissue protection and tissue destruction.
Intracellular microorganisms, in particular viruses, cause the downregulation of expression of MHC class I molecules as a mechanism of immune evasion to prevent the destruction of infected cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). The host, in turn, upregulates expression by infected cells of interleukin-15 (IL-15) and the non-classical MHC class I molecules such as MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A (MICA), which is recognized by the activating natural killer (NK) receptor NKG2D (natural killer group 2, member D). Together, this leads to a reduced T cell receptor (TCR) activation threshold and to lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) activity in CTLs. CTLs can hence destroy infected cells despite low levels of or absent MHC class I expression. Furthermore, effector CTLs are rendered resistant to the effects of forkhead box P3 (FOXP3)+ regulatory T (TReg) cells and transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) in the presence of IL-15. Once the infected cells are eliminated and replaced by healthy cells, CTLs return to a `resting state' and again become sensitive to immune regulation. In the context of autoimmunity, MHC class I molecules are not downregulated, and the expression of IL-15 and MICA is constitutive for unknown reasons. This leads to the chronic activation of CTLs and ongoing tissue destruction. By contrast, tumours — in addition to expressing TGFβ and PDL1, which is the ligand for the inhibitory receptor PD1 (programmed cell death protein 1) — also lack surface expression of IL-15 and MICA. Hence, CTLs lack the necessary activating signals as well as being sensitive to the inhibitory signals present in the tumour environment, resulting in a lack of CTL-mediated killing of tumour cells. γc, common cytokine receptor γ-chain; IL-2/IL-15Rβ, IL-2/IL-15 receptor β-subunit; IL-15Rα, IL-15 receptor α-subunit.