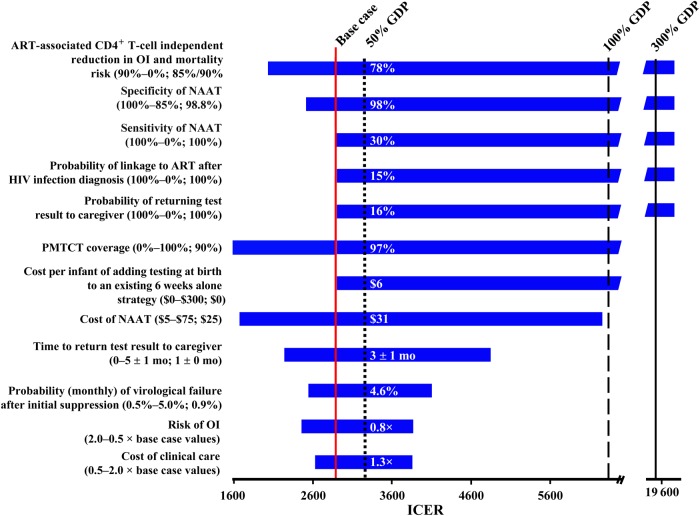
Figure 2.
Tornado diagram showing key parameters that change the cost-effectiveness of diagnostic testing for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection during early infancy (commonly known as “early infant HIV diagnosis” [EID]) at birth and 6 weeks of age (hereafter, the “birth and 6 weeks” strategy), compared with testing at 6 weeks of age alone (hereafter, the “6 weeks alone” strategy). Key parameters varied in model sensitivity analyses are shown on the left. Values in parentheses indicate the range examined (from the value leading to the lowest incremental cost-effectiveness ratio [ICER] to the value leading to the highest ICER), with base-case values after the semicolon. ICERs for the comparison of birth and 6 weeks strategy versus the birth alone strategy are shown on the horizontal axis in 2013 dollars per year of life saved (YLS). The range of ICERs for each varied parameter is indicated by the blue bars. Longer bars indicate parameters to which the model results were more sensitive. The red line indicates the ICER of $2900/YLS for the birth and 6 weeks strategy versus EID at birth alone, using all base-case parameters. The dotted black line indicates 50% of South Africa's per capita gross domestic product (GDP; 0.5 × $6500 = $3250), the dashed black line indicates 100% of South Africa's per capita GDP ($6500), and the solid black vertical line indicates 300% of South Africa's per capita GDP ($19 500). The value for each parameter at which the ICER crosses the 50% GDP threshold is listed within each horizontal bar. This figure provides a framework for making decisions on cost-effectiveness grounds: the value within the horizontal bar indicates when one would favor the 6 weeks alone strategy over the birth and 6 weeks strategy on the basis of this criterion. Bars extending to the far-right axis indicate scenarios in which the birth and 6 weeks strategy results in an ICER of >$20 000/YLS, compared with the 6 weeks alone strategy, or becomes strongly dominated (more expensive and less effective) by the 6 weeks alone strategy. Abbreviations: ART, antiretroviral therapy; NAAT, nucleic acid amplification test; OI, opportunistic infection; PMTCT, prevention of mother-to-child transmission.