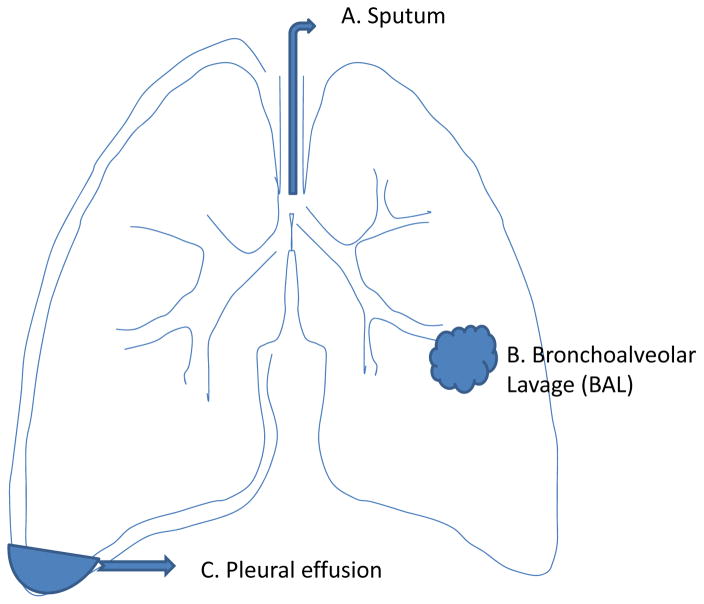
Figure 3.
Anatomical structures of the lung and the production of potential fluid-based samples. (A) Sputum is a fluid secreted by bronchial epithelial cells from lower airways. It is usually collected as spontaneous and/or induced sputum. (B) Numerous proteins are secreted or leaked into the alveolar space from lung parenchymal cells. Proteins in the alveolar space can be recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) using bronchoscopy. (C) The pleural cavity is a space between the lung and chest wall. A large amount of fluid, known as pleural effusion, can accumulate in the pleural cavity in a variety of diseases including lung cancers, particularly when the tumor metastases to the pleural cavity.