Figure 2.
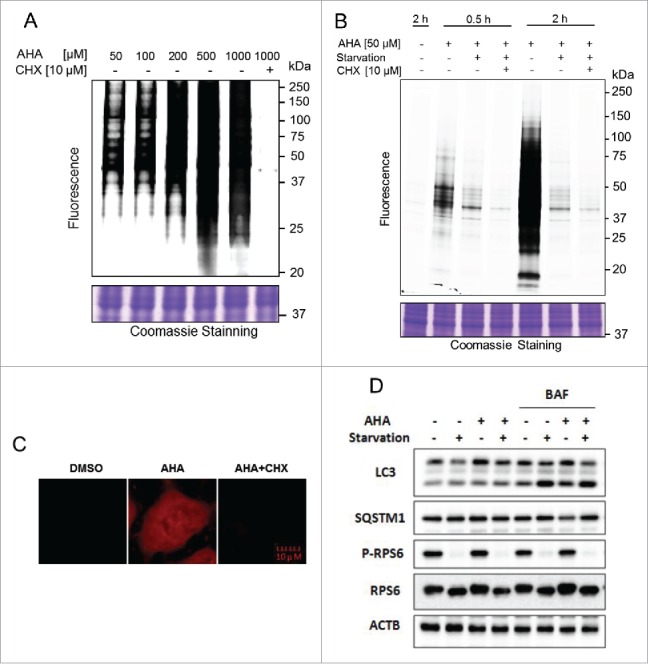
Optimization of AHA labeling of newly synthesized proteins during autophagy. (A) Dosage-dependent increase of AHA-labeled de novo proteins. HeLa cells were labeled with varying doses of AHA, ranging from 50 µM to 1 mM, or in combination with CHX (10 µM) for 30 min under normal growth conditions. Intensity of AHA-labeled proteins was observed in gel fluorescence. (B) Time-dependent increase in AHA labeling. Cells were cultured in methionine-free DMEM with 10% dialyzed fetal bovine serum and labeled with AHA (50 µM) with or without CHX (10 µM) for different times. Starvation was performed in amino acid-free medium. Intensity of AHA-labeled proteins was also observed in gel fluorescence. (C) HeLa cells were labeled with AHA (50 µM) with or without CHX (10 µM) for 2 h during autophagy induction. Intensity of AHA-labeled proteins was shown under a confocal microscope. (D) Autophagy flux level change in AHA-labeled cells. HeLa cells were labeled with AHA (50 µM) in methionine-free medium or amino acid-free medium in the presence or absence of bafilomycin A1 (BAF, 25 nM) for 2 h, and cell lysates were prepared for immunoblotting of LC3, SQSTM1, phospho (p)-RPS6 and RPS6. ACTB served as a loading control.
