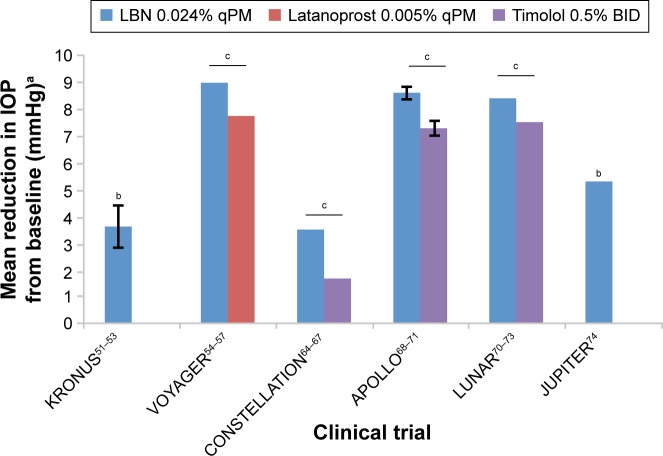
Figure 3.
Mean reduction in IOP from baseline associated with LBN 0.024% qPM, latanoprost 0.005% qPM, and timolol 0.5% BID from six major clinical trials.
Notes: Error bars represent standard deviation (if reported). aReduction in mean diurnal IOP at the study’s primary endpoint, with the exception of data from JUPITER, in which IOP was measured only once on study visit days. For trials with multiple primary endpoints (APOLLO and LUNAR), the maximal mean reduction from baseline in diurnal IOP is presented. bStatistically significantly different from baseline IOP. cSignificantly different from comparator arm. Adapted by permission from BMJ Publishing Group Limited. A randomised, controlled comparison of latanoprostene bunod and latanoprost 0.005% in the treatment of ocular hypertension and open angle glaucoma: the VOYAGER study. Weinreb RN, Ong T, Scassellati Sforzolini B, et al. Br J Ophthalmol. © 2015;99(6):738–745.54
Abbreviations: IOP, intraocular pressure; LBN, latanoprostene bunod; qPM, every evening; BID, twice daily.