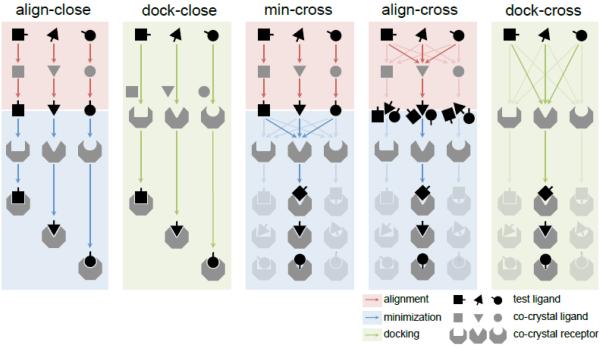
Figure 1. “Close” and “cross” methods for affinity ranking and pose prediction.
Align-close and dock-close methods minimize and dock to the “closest” receptor for each compound. Min-cross, align-cross and dock-cross methods minimize and dock to all available receptors and select “optimal” receptor based on available experimental data (see Methods). This is shown in the figure by the greyed-out shapes in the “cross” methods that ultimately select one optimal receptor. Red blocks and arrows correspond to alignment, blue blocks and arrows correspond to minimization, green blocks and arrows correspond to docking.