Abstract
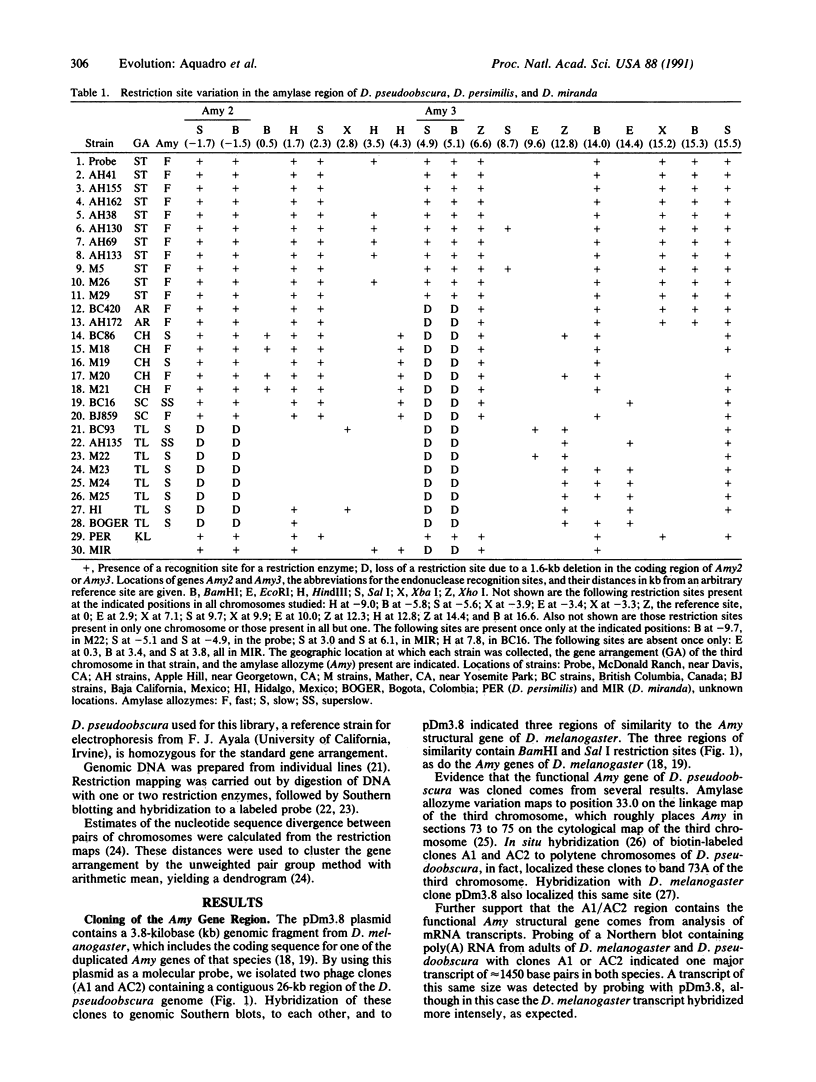
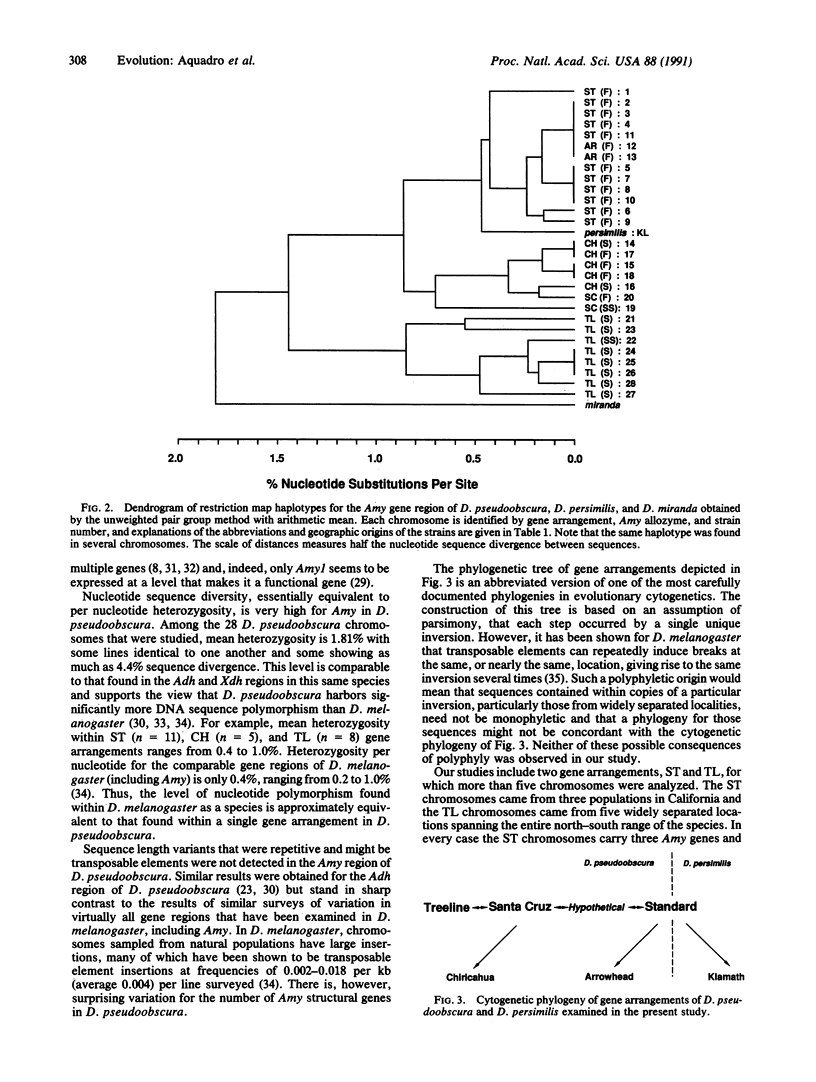
The amylase region of the third chromosome of Drosophila pseudoobscura has been cloned and localized to cytological band 73A. It is contained within a series of highly polymorphic inversions and serves as a convenient tool for a molecular evolutionary analysis of the inverted gene arrangements. Amylase in D. pseudoobscura is a family of three genes, and some chromosomes have deletions for one or two of them. Two overlapping clones covering 26 kilobases were isolated and used as probes to survey DNA restriction map polymorphism among 28 lines, representing five of the major inversion types found in natural populations, as well as single chromosomes from the closely related species Drosophila persimilis and Drosophila miranda. Restriction-site differences are considerably greater among the various gene arrangements than among chromosomes with the same gene arrangement. Clustering the restriction map haplotypes yielded a dendrogram concordant with the phylogeny generated independently from cytogenetic considerations. The inversion polymorphism is estimated to be about 2 million years old.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. W. Selection in natural and experimental populations of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genome. 1989;31(1):239–245. doi: 10.1139/g89-041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Aquadro C. F., Anderson W. W. DNA sequence evolution of the amylase multigene family in Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetics. 1990 Sep;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccone A., Amato G. D., Powell J. R. Rates and patterns of scnDNA and mtDNA divergence within the Drosophila melanogaster subgroup. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):671–683. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chovnick A. Gene conversion and transfer of genetic information within the inverted region of inversion heterozygotes. Genetics. 1973 Sep;75(1):123–131. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doane W. W., Gemmill R. M., Schwartz P. E., Hawley S. A., Norman R. A. Structural organization of the alpha-amylase gene locus in Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila miranda. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1987;14:229–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobzhansky T., Epling C. The Suppression of Crossing Over in Inversion Heterozygotes of Drosophila Pseudoobscura. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1948 Apr;34(4):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.34.4.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W. R. The P family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:315–344. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmill R. M., Levy J. N., Doane W. W. Molecular cloning of alpha-amylase genes from Drosophila melanogaster. I. Clone isolation by use of a mouse probe. Genetics. 1985 Jun;110(2):299–312. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley S. A., Norman R. A., Brown C. J., Doane W. W., Anderson W. W., Hickey D. A. Amylase gene expression in intraspecific and interspecific somatic transformants of Drosophila. Genome. 1990 Aug;33(4):501–508. doi: 10.1139/g90-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. N., Gemmill R. M., Doane W. W. Molecular cloning of alpha-amylase genes from Drosophila melanogaster. II. Clone organization and verification. Genetics. 1985 Jun;110(2):313–324. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery E., Charlesworth B., Langley C. H. A test for the role of natural selection in the stabilization of transposable element copy number in a population of Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1987 Feb;49(1):31–41. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300026707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Non-random association between electromorphs and inversion chromosomes in finite populations. Genet Res. 1980 Feb;35(1):65–83. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001394x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovsky O., Dobzhansky T. Genetics of natural populations. XXXVII. The coadapted system of chromosomal variants in a population of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetics. 1966 May;53(5):843–854. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.5.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. R. Population genetics of Drosophila amylase. II. Geographic patterns in D. pseudoobscura. Genetics. 1979 Jun;92(2):613–622. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S., Lewontin R. C. A molecular approach to the study of genic heterozygosity in natural populations. 3. Direct evidence of coadaptation in gene arrangements of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):398–405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S., Lewontin R. C. A molecular approach to the study of genic heterozygosity in natural populations. V. Further direct evidence of coadaptation in inversions of Drosophila. Genetics. 1971 Nov;69(3):405–408. doi: 10.1093/genetics/69.3.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S., Lewontin R. C., Hubby J. L. A molecular approach to the study of genic heterozygosity in natural populations. IV. Patterns of genic variation in central, marginal and isolated populations of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetics. 1969 Apr;61(4):841–858. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M. A., Hallas M. E., Lewontin R. C. Distinguishing the forces controlling genetic variation at the Xdh locus in Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetics. 1989 Oct;123(2):359–369. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer S. W., Aquadro C. F., Anderson W. W. Restriction-map variation in the alcohol dehydrogenase region of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 May;4(3):254–265. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer S. W., Aquadro C. F. Nucleotide sequence of the Adh gene region of Drosophila pseudoobscura: evolutionary change and evidence for an ancient gene duplication. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):61–73. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley D. G., Anderson W. W., Schaffer H. E. Gene Frequency Changes at the alpha-Amylase Locus in Experimental Populations of DROSOPHILA PSEUDOOBSCURA. Genetics. 1977 Oct;87(2):357–369. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


