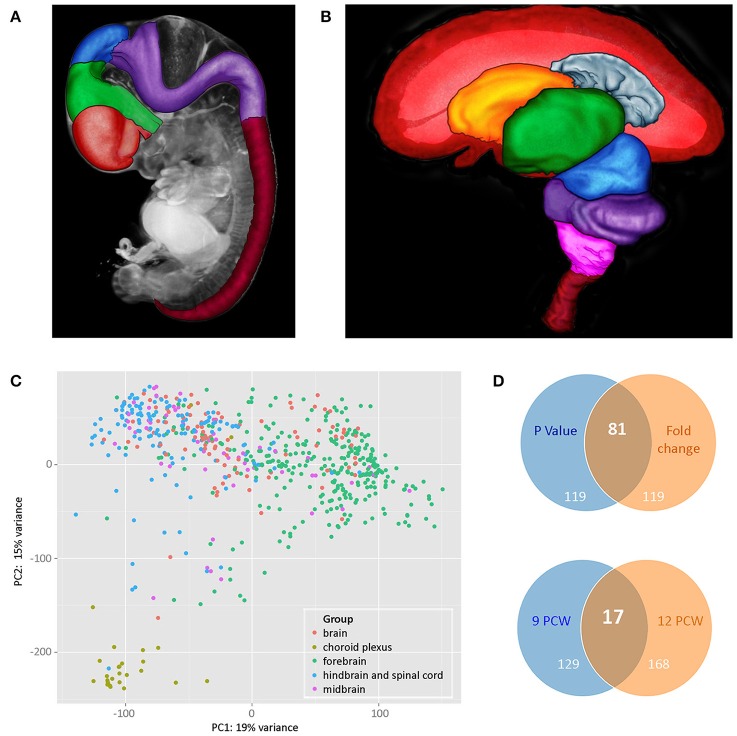
Figure 1.
(A,B) Illustrate brain regions at two developmental stages: (A) 7 PCW. Regions of the brain plus the spinal cord have been defined in a 3 dimensional (3D) model of a Carnegie Stage 19 (CS19) embryo generated by optical projection tomography (Sharpe et al., 2002). Red—telencephalon, green—diencephalon, blue—midbrain, purple—hindbrain, deep red—spinal cord, gray—rest of head, and body. (B) 10 PCW. A 3D model of the brain and part of the spinal cord was generated by magnetic resonance imaging and brain regions defined. The front of the brain is on the left. In the image, the left cerebral cortex has been removed to show the inner view of the right cerebral cortex plus the inner structures of the telencephalon (choroid plexus and basal ganglia) as well as structures that lie between the two cerebral cortexes (diencephalon and midbrain) which are fully or partially hidden when looking at a whole brain of this age. Red—cerebral cortex, gray—cerebral choroid plexus, orange—basal ganglia, green—diencephalon, blue—midbrain, purple—cerebellum and pons, pink—medulla oblongata, deep red—upper part of spinal cord. For both images, the 3D models were visualized and brain regions were defined using MAPaint, custom-designed software from the Edinburgh Mouse Atlas Project team3. (C) Shows principal component analysis (PCA) analysis carried out on all RNAseq datasets. Choroid plexus samples (khaki green) provide the most distinct set. Forebrain (green) and hindbrain (blue) samples separated out but with some slight overlap. Midbrain samples (purple) and unidentified brain samples (red) fell within the forebrain and hindbrain clusters. (D) Shows Venn diagrams comparing genes that are differentially expressed in a subset of RNAseq data sets from cortical samples at 9 and 12 PCW. The upper panel compares the top 200 genes expressed differentially between 9 and 12 PCW (anterior, central, posterior, and temporal cortex samples grouped for each age) where the expression differences had the lowest p-values with the top 200 differentially expressed genes with the largest fold changes. There were 81 genes that were identified as differentially expressed between 9 and 12 PCW where the expression differences had both the lowest p-values and showed the highest fold change. All 200 genes with the largest fold change had a p-value < 0.05. The lower panel compares genes differentially expressed between anterior and posterior cortex at the two stages. At 9 PCW, 146 genes were differentially expressed between the anterior and posterior cortex. At 12 PCW, 185 genes were differentially expressed between the anterior and posterior cortex. 17 of these genes were differentially expressed between the anterior and posterior cortex at both 9 and 12 PCW. The lists of differentially expressed genes corresponding to those summarized in the upper and lower panels are shown in Supplementary Tables 3, 4, respectively, on the HDBR website.