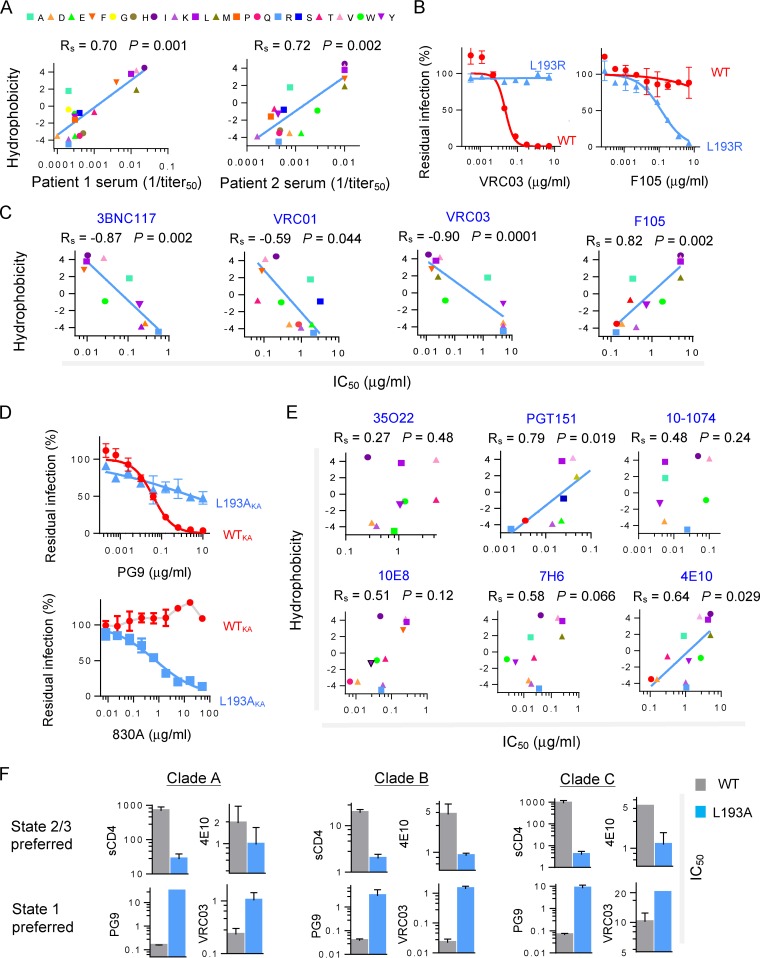
FIG 4 .
Neutralization of HIV-1 variants differing in conformational state by human antibodies elicited during infection. (A) Recombinant viruses with Envs containing substitutions in residue 193 were tested for sensitivity to neutralization by antibodies. The relationship between the hydrophobicity of residue 193 and sensitivity to neutralization by polyclonal sera (PS) from two HIV-1-infected individuals is shown. (B) Neutralization of WT and L193R HIV-1JR-FL by two different types of CD4-BS antibodies: the bNAb VRC03 and the weakly neutralizing F105 antibody. (C) Relationship between the hydrophobicity of Env residue 193 and HIV-1JR-FL sensitivity to neutralization by four CD4-BS antibodies: three bNAbs (3BNC117, VRC01, and VRC03) and one weakly neutralizing antibody, F105. (D) Sensitivity of viruses with the indicated Env variants to neutralization by the PG9 antibody. The Env variants tested have changes distant from the defined V1/V2 binding site of the PG9 antibody (62). All these variants have, in addition, the E168K-plus-N188A changes that are required for the binding of PG9 to the HIV-1JR-FL Env (51). (E) The relationship between the hydrophobicity of Env residue 193 and HIV-1JR-FL sensitivity to neutralization by bNAbs directed against gp120-gp41 hybrid epitopes (35O22 and PGT151), a V3 glycan-dependent epitope (10-1074), and gp41 MPER epitopes (10E8, 7H6, and 4E10) is shown. (A, C, and E) Spearman’s Rho coefficient and two-tailed P values are shown. (F) Conformation-selective bNAbs and sCD4 were used to test the sensitivity of the WT and the L193A variant of HIV-1 strains BG505 (clade A), JR-FL (clade B), and ZM53M.PB12 (clade C). For PG9 neutralization, the E168K + N188A mutant of HIV-1JR-FL was used. Reported IC50 units are nanomolar (nM) for sCD4 and micrograms per milliliter (μg/ml) for the bNAbs. Data shown are averages of results obtained in two or three independent experiments.