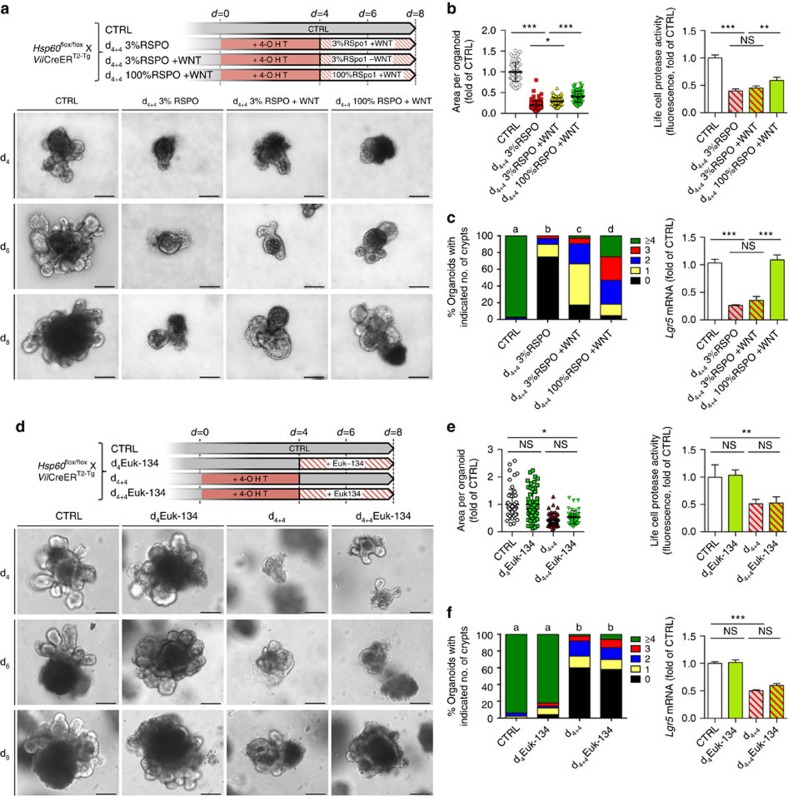
Figure 9. WNT10A and RSPO1 but not ROS scavenging rescues intestinal organoid growth after Hsp60 knockout.
Organoids were isolated from Hsp60flox/flox, VillinCreERT2-Tg mice and distributed to four protocols. (a) Experimental scheme to show the effects of RSPO1 and WNT10A supplementation (100 ng ml−1) on Hsp60-deficient small intestinal organoids. Lower panel: representative pictures of the indicated treatments and time points. (b) Measurement of organoid area (left; N>60 per treatment) and life cell protease activity measured by fluorescence (right) following indicated treatments. (c) Quantification of de novo crypt formation (left); (a–d) significantly different from each other, Kruskal–Wallis test on ranks followed by Dunn's test. Right: qRT–PCR analysis of Lgr5 mRNA expression in organoids in response to WNT10A treatment. (d) Experimental scheme to show the effects of the ROS scavenger Euk-134 (100 μM) on Hsp60-deficient small intestinal organoids. Lower panel: representative pictures of the indicated treatments and time points. (e) Organoid area (left; N>60 per treatment) and life cell protease activity measured by fluorescence (right) following indicated treatments. (f) Quantification of de novo crypt formation (left); (a,b), significantly different from each other, Kruskal–Wallis test on ranks followed by Dunn's test. Right: qRT–PCR analysis of Lgr5 mRNA expression in organoids in response to Euk-134 treatment. Bars represent mean+s.e.m. Asterisks indicate significant differences *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; NS, not significant. Unless otherwise indicated, one-way analysis of variance and appropriate post hoc tests were used for all statistical analyses. Data from organoid experiments derive from at least three independent experiments. Scale bars, 200μm.