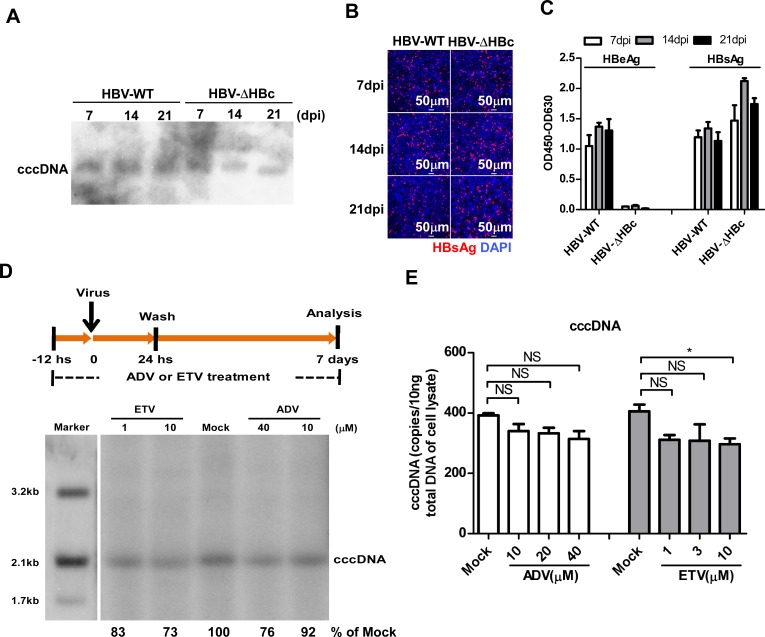
Fig 2. HBV DNA polymerase activity is dispensable for cccDNA biosynthesis in a de novo infection.
(A-C) HepG2-NTCP cells were infected with a multiplicity of 100 genome equivalents (mge) of wild-type or HBcAg-deficient (HBV-ΔHBc) virus. On the indicated time points after infection, HBV cccDNA was determined by Southern blot analysis (A). Intracellular HBsAg was stained with mcAb 17B9 (red) and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Images were taken with a Nikon A1-R confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 50 μm (B). Secreted HBeAg and HBsAg were measured by ELISA (C). Data are representatives of three independent experiments. (D-E) HepG2-NTCP cells were mock-treated or treated with the indicated concentrations of adefovir (ADV) or entecavir (ETV) from 12 h before HBV-ΔHBc infection to 7 dpi as depicted in the top panel (D). HBV cccDNA in the infected cells were detected by Southern blot analysis (D). The intensity of HBV cccDNA bands were determined by Image J and the relative amounts of cccDNA were expressed as the percentage of that in the mock-treated control cells. HBV cccDNA was also quantified by a qPCR assay (E). Data are representatives of three independent experiments. Data were analyzed by an unpaired two-tailed t test. NS: non-significant; * p<0.05.