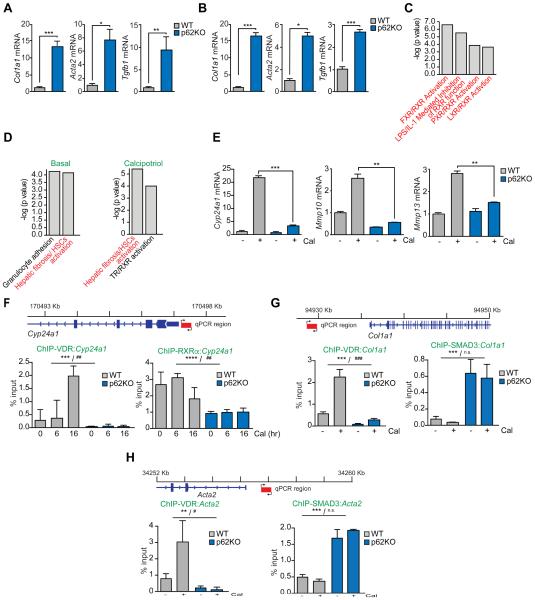
Figure 5. p62 is required for hepatic stellate activation and VDR function.
(A and B) qPCR analysis of mRNA of HSC activation markers in primary quiescent (A) or immortalized activated (B) WT and p62KO HSC. (C) Nuclear-receptor-related pathways from Ingenuity analysis (IPA) of downregulated genes in liver tumors of total p62KO and WT mice described in Figure 1A. (D) Top canonical pathways from Ingenuity analysis (IPA) of differentially expressed genes between p62KO and WT HSC in basal conditions and upon calcipotriol (Cal) treatment. (E) qPCR analysis of mRNA of Cyp24a1, Mmp10, and Mmp13 in WT and p62KO HSC. (F) Primer design and ChIP-qPCR analysis of Cyp24a1 promoter occupancy of VDR and RXRα. (G) Primer design and ChIP-qPCR analysis of Col1a1 promoter occupancy of VDR and SMAD3. (H) Primer design and ChIP-qPCR analysis of Acta2 promoter occupancy of VDR and SMAD3. Results are presented as mean ± SEM. p values were calculated using a two-way ANOVA; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 for all comparisons of p62KO versus WT; #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001, n.s. non-significant, for all comparisons of Cal versus vehicle. See also Figure S4.