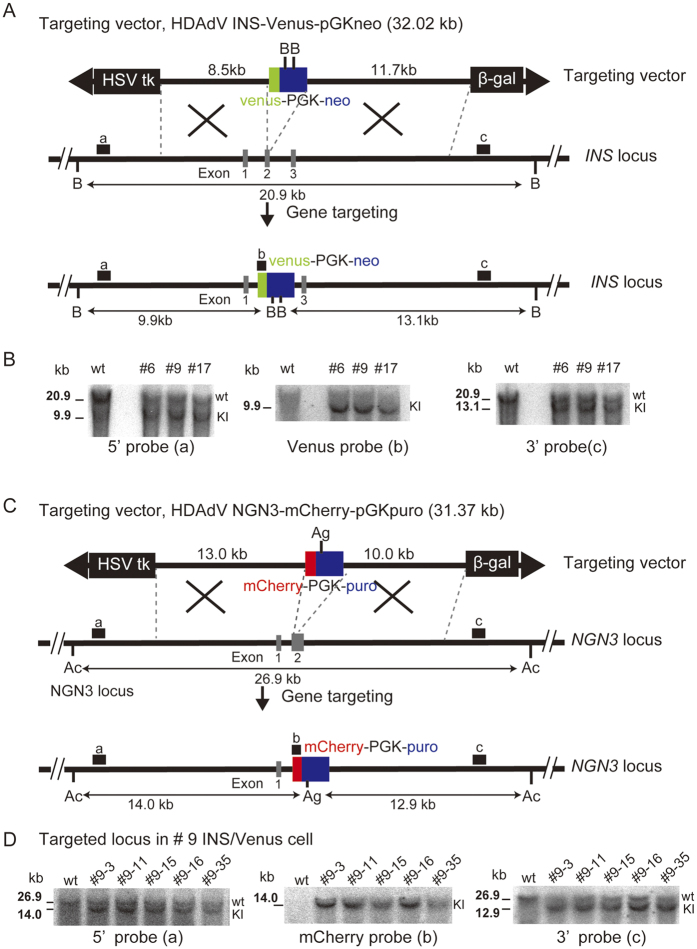
Figure 1. Gene targeting at the INS and NGN3 loci in hiPSCs.
(A) Schematic illustration of INS knockout with HDAdV. The structures of the targeting vector (HDAdV-INS-Ve-pGK-Neo), the wild-type human INS locus, and the targeted locus are shown. Venus cDNA was inserted under the INS promoter at the ATG of the coding region (at exon 2; exons are shown as grey boxes and numbered 1–3). Venus cDNA: the expression cassette for Venus (yellow fluorescent protein gene). HSVtk: the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene cassette. BstXl sites (B) are indicated; probes a, b, and c indicate the 5′ probe, Venus probe, and 3′ probe used for Southern blotting analysis, respectively. (B) The targeted hiPSC clones (#6, 9, and 17) were analysed by Southern blotting with the 5′ probe (a) (9.9 kb), Venus probe (b) (9.9 kb), and 3′ probe (13.1 kb). (C) To target NGN3-mCherry, we chose clone #9 of the INS-Venus-targeted hiPSCs. The structure of the targeting vector for NGN3-mCherry (HDAdV-NGN3-mcherry-pGK-puro) is shown. mCherry cDNA was inserted under the control of the NGN3 promoter at ATG of the coding region (at exon 2; exons are shown as grey boxes numbered 1 and 2). AccI (Ac) and AgeI (Ag) sites are indicated, and probes a, b, and c indicate the 5t probe, mCherry probe, and 3p probe used for Southern blotting analysis, respectively. (D) The targeted hiPSC clones (#9–3, 9–11, 9–15, 9–16, and 9–35) were analysed by Southern blotting analysis with the 5′ probe (a) (14.0 kb), mCherry probe (b) (14.0 kb), and 3′ probe (c) (12.9 kb). Uncropped versions of the scans are presented in Supplementary Fig. S6. HDAdV: helper-dependent adenoviral vector.