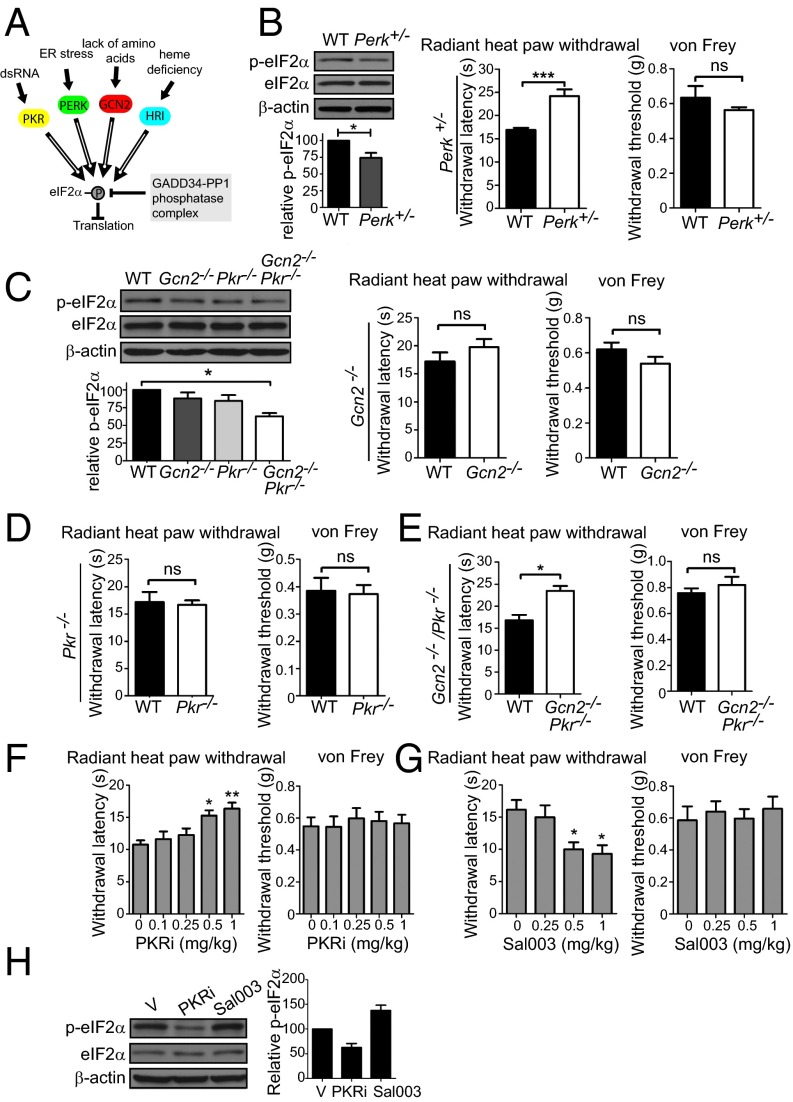
Fig. 3.
eIF2α kinases control thermal threshold. (A) eIF2α kinases and phosphatase GADD34/PP1 (growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible 34/protein phosphatase1). (B) Perk+/− mice show a decrease in p-eIF2α (n = 4 mice per genotype, P < 0.05) and in noxious heat sensitivity (n = 4 males and 4 females per genotype, P < 0.001). Gcn2−/− and Pkr−/− mice show no alteration in thermal latencies (C and D, respectively; n = 4 males and 4 females per genotype, P > 0.05). (E) Gcn2−/− Pkr−/− double KO mice show reduced noxious heat sensitivity (n = 3 males and 4 females per genotype, P < 0.05). eIF2α phosphorylation in DRGs of Gcn2−/−, Pkr−/−, and Gcn2−/− Pkr−/− double KO mice is shown in C (n = 3 mice per genotype). PKR inhibitor (PKRi) (F) and Sal003 (G) were injected i.p. for 3 d daily, and thermal and mechanical thresholds were measured 30 min after the last injection (n = 4 males and 4 females per condition). (H) eIF2α phosphorylation in DRGs of mice injected with PKRi (1 mg/kg) and Sal003 (1 mg/kg) is shown (n = 5 mice per drug). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant by Student t test and Bonferroni post hoc test following one-way ANOVA.