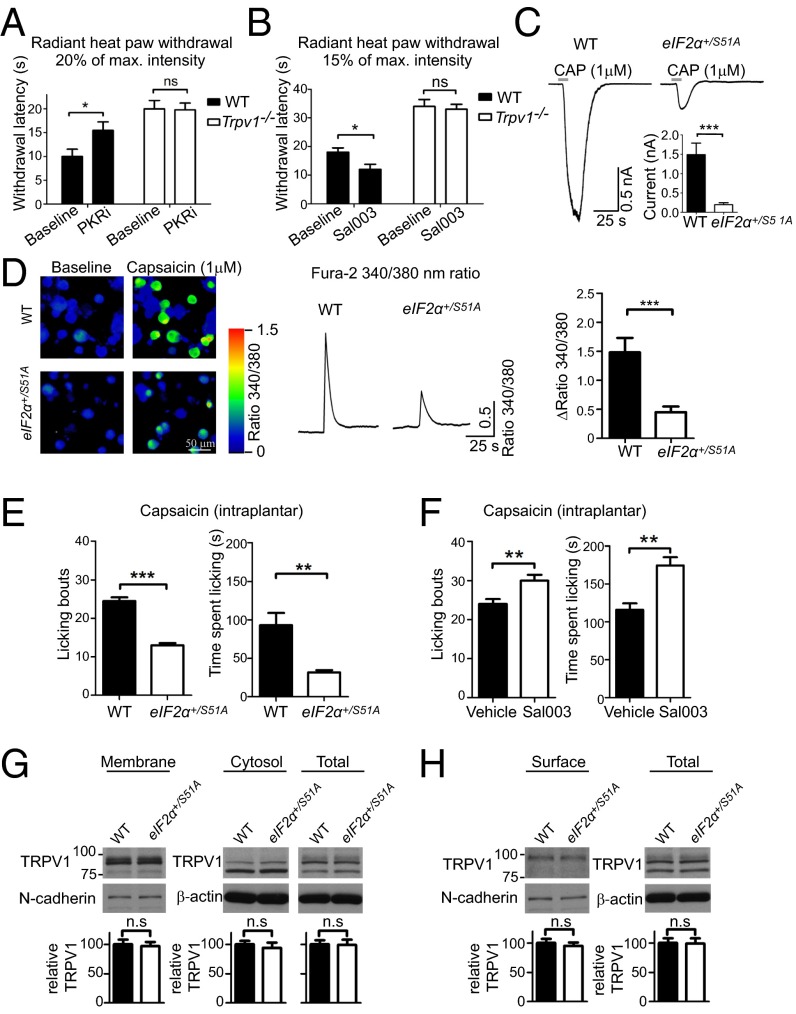
Fig. 4.
eIF2α phosphorylation regulates thermal threshold via TRPV1. Modulation of eIF2α phosphorylation in Trpv1−/− mice does not alter heat sensation. PKRi (1 mg/kg for 3 d daily, i.p.) elevates thermal threshold in WT but not in Trpv1−/− mice (A; n = 4 males and 4 females per genotype-drug condition). Sal003 (1 mg/kg for 3 d daily, i.p.) decreases thermal threshold in WT but not in Trpv1−/− mice (B, n = 4 males and 4 females per genotype-drug condition). For the radiant heat paw withdrawal test, the light beam was set to 20% of the maximal intensity in A and to 15% in B. Capsaicin (1 μM) evokes smaller currents (C, n = 12 cells for eIF2α+/S51A and 10 for WT, from three different neuronal cultures per genotype) and smaller calcium transients (D, n = 72 cells for eIF2α +/S51A and n = 46 cells for WT, from four different neuronal cultures per genotype, using Fura-2 340/380-nm ratio) in cultured DRG neurons prepared from eIF2α+/S51A compared with WT mice. Capsaicin (2.5 μg), injected s.c. into the plantar surface of the hindpaw, elicited less nocifensive behaviors in eIF2α+/S51A compared with WT mice (E; n = 4 males and 4 females per genotype or drug), whereas in mice injected with Sal003 (1 mg/kg for 3 d daily, i.p.) capsaicin-induced pain behavior is increased (F). Western blot analysis shows that the TRPV1 protein levels are not altered in membrane and cytosolic fractions, as well as in total lysates of DRGs of eIF2α+/S51A mice (G; n = 4 mice and genotype). TRPV1 surface levels were measured in DRG cultured neurons prepared from eIF2α+/S51A and WT mice using surface biotinylation assay (H; n = 3/group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Student t test and Student t test following two-way (genotype × drug) ANOVA.