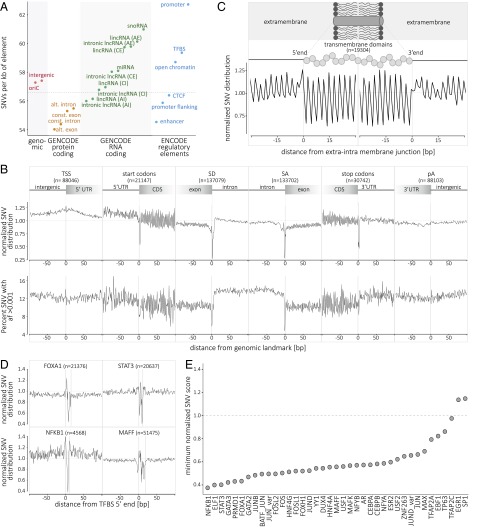
Fig. 2.
Single-nucleotide variant distribution and metaprofiles in the coding and noncoding genome. (A) Distribution of SNVs in selected genomic elements (genomic, protein-coding, RNA-coding, and regulatory elements; see SI Appendix for details). The genome average of 56.59 SNVs per kb is indicated by the horizontal dashed line. (B) The metaprofiles of protein-coding genes are created by aligning all elements of six different genomic landmarks (TSS, start codon, SD, SA, stop codon, and pA) for all 10,545 genomes. The y axis (Upper) describes the enrichment/depletion of SNV occurrence per position (count score; SI Appendix, Fig. S7), normalized to the mean of the protein-coding score (indicated by the horizontal dashed line); the y axis (Lower) describes the percent of SNVs at each position with an allelic frequency higher than 1 in 1,000 (frequency score; SI Appendix, Fig. S8). The x axis represents the distance from the genomic landmark. The vertical lines indicate the genomic landmark position. The SD and SA metaprofiles highlight the strong conservation of the splice sites (Upper) and the difference in SNV allele frequency between exons and introns (Lower). (C) The metaprofile of transmembrane domains is created by aligning all single domains at their 5′ and 3′ ends. The figure highlights that every amino acid in the transmembrane domain is conserved compared with the surrounding structure of the protein. (D) The metaprofiles of TFBSs are created by aligning all of the binding sites of four transcription factors (FOXA1, STAT3, NFKB1, and MAFF) for all 10,545 genomes. The x axis represents the distance from the 5′ end of the TFBS. The vertical lines indicate the 5′ and 3′ ends of the TFBS. (E) Ranking of 39 TFBSs by conservation (minimum score for the motif; i.e., the nucleotide with the lowest tolerance to variation). For C–E, the y axis describes the normalized enrichment/depletion of SNV occurrence per position, normalized to the mean of the protein-coding score (indicated by the horizontal dashed line). AE, alternative exon; AI, alternative intron; CE, constitutive exon; CI, constitutive intron; oriC, origin of replication; pA, polyadenylation site; SA, splice acceptor site; SD, splice donor site; TSS, transcription start site.