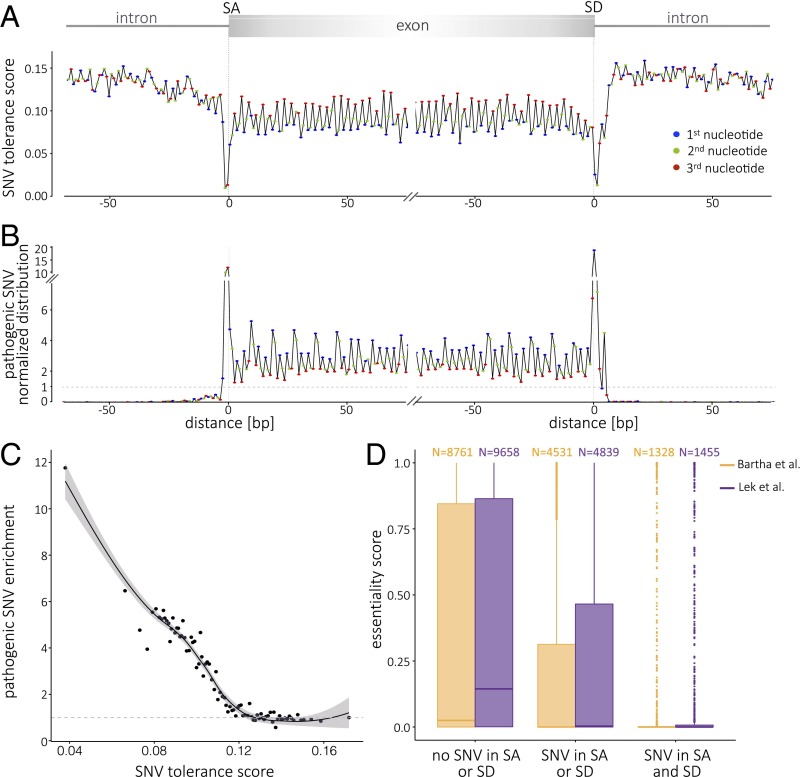
Fig. 3.
Relationship of a metaprofile tolerance score with variant pathogenicity and gene essentiality. (A) Metaprofile of the transition between introns and exons expressed as the tolerance score (TS). The TS is the product of the normalized SNV distribution value by the proportion of SNVs with allele frequency ≥0.001 (Fig. 2B). The exon sequence highlights the conservation and tolerance to variation of the third position in codons (red). The pattern of higher tolerance to variation every third nucleotide is lost in introns. The TS is lowest at the splice donor and acceptor sites and highest in introns. (B) The distribution of ClinVar and HGMD pathogenic SNVs (n = 29,808 in SD; n = 30,369 in SA metaprofiles) reflects a significant enrichment of pathogenic variants at the sites of lowest TS. Consistently, the exon sequence highlights the enrichment for variation at the first position in codons (blue), as it results in amino acid change or truncation. (C) Relationship of tolerance score and enrichment for pathogenic variants. Represented on the x axis are the mean TS values for the coding region (±10 bp of intergenic or intronic boundaries); each dot represents the mean of 10 positions. The y axis represents the fold enrichment in pathogenic variants. local regression (LOESS) curve fitting is represented by the solid line; the shaded area indicates the 95% confidence interval. (D) Less essential genes tolerate variation at sites with lowest TS values. The x axis represents three different classes of genes according to their having evidence for splice acceptor/donor variation. The y axis represents essentiality scores of Bartha et al. (21) (yellow) and Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC) pLI (probability that a gene is intolerant to a loss of function mutation) (22) (purple). The large majority of genes that tolerate splice-site variants are not essential; in contrast, there is a marked shift to higher essentiality values for genes that are not observed to be variant at the splice sites.