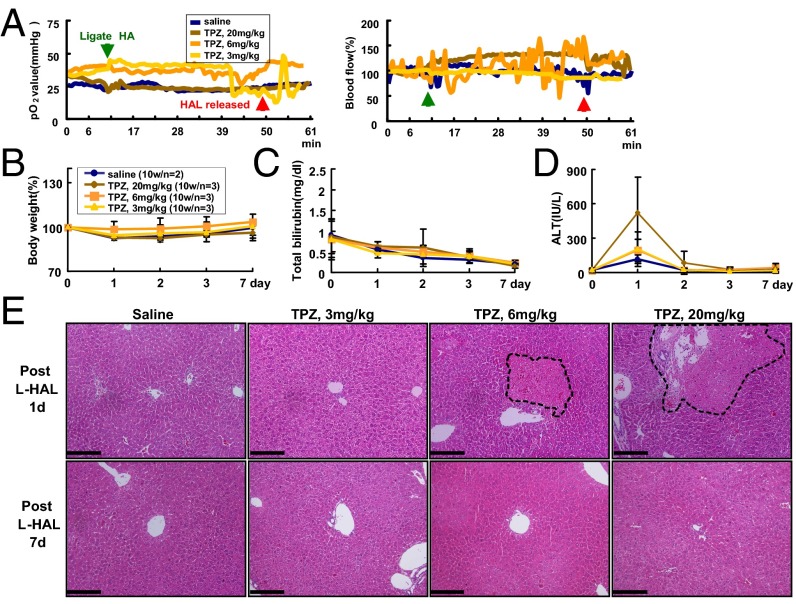
Fig. 2.
Dose escalation study of TPZ combined with transient L-HAL in C57BL/6 mice. The mice were treated with 0.9% saline or three doses of TPZ, 3, 6, and 20 mg/kg, through tail vein injections before transient L-HAL. (A) Transient L-HAL could not induce hypoxia in the left lobe of wild-type mouse liver. The green arrow indicates the time when L-HAL was initiated, and the red arrow indicates the time when L-HAL was released. All groups exhibited similar changes in body weights (B) and total bilirubin levels (C). (D) An elevation of the ALT levels was observed on day 1 in mice that were treated with 20 mg/kg TPZ. (E) Histopathological examination of the mouse livers. The liver tissues were collected from transient L-HAL–treated liver lobes from each group after 1 d (Upper) or 7 d (Lower) of treatment and were processed for H&E staining. The data are representative of each independent group. The black dashed circle indicates the necrotic region. (Scale bars: 0.2 mm.)