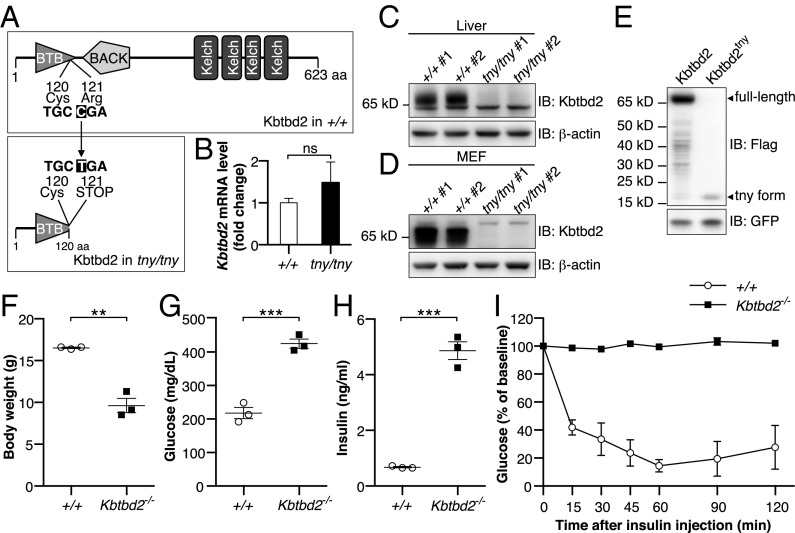
Fig. 2.
Mutations of Kbtbd2 cause the tny phenotype. (A) Protein domains of WT mouse KBTBD2 (Upper) and position of tny mutation (Lower). The tny mutation is an arginine to premature stop codon substitution at position 121 of the protein. (B) Relative Kbtbd2 mRNA level (normalized to Actb mRNA) measured by RT-qPCR of mRNA isolated from livers of three male homozygous tny mice or WT littermates. (C and D) Immunoblots of liver (C) and MEF (D) lysates from two male homozygous tny mice and WT littermates. (E) Immunoblots of lysates of 293T cells expressing 3×FLAG-tagged full-length WT KBTBD2 or KBTBD2tny. GFP was coexpressed as a loading control. (F–H) Body weight (F), blood glucose (G), and serum insulin (H) values in 6-wk-old male homozygous Kbtbd2 KO (Kbtbd2−/−) and WT littermates. Glucose and insulin were measured after a 6-h fast. (I) Insulin tolerance test. Blood glucose was measured at indicated times after i.p. insulin injection in male Kbtbd2−/− mice (n = 4) and WT littermates (n = 3) at 16 wk of age. The baseline blood glucose levels (0 min) of Kbtbd2−/− mice and WT littermates were 728 ± 18 mg/dL and 298 ± 28 mg/dL, respectively. In F–H, data points represent individual mice. P values were determined by Student’s t test.