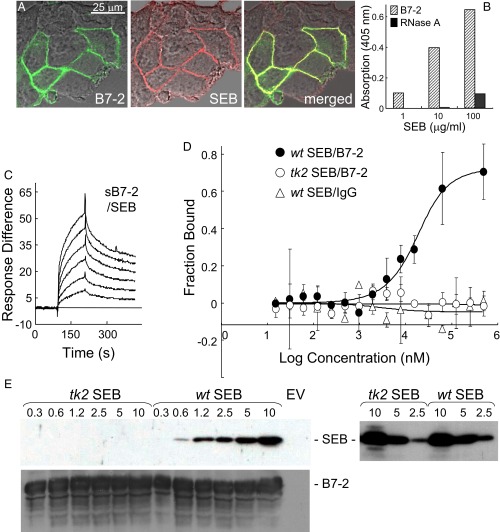
Fig. 2.
Superantigen binds B7-2 directly. (A) Colocalization of SEB with cell-surface B7-2. Representative field of confocal microscopy is shown. HEK 293T cells were transfected to express B7-2–GFP fusion protein (green) and after 24 h incubated for 30 min with Alexa-Fluor-633–labeled SEB (red). (B) Binding of SEB to immobilized sB7-2 (5 μg/mL), but not to immobilized ribonuclease A (5 μg/mL), determined with anti–SEB-HRP antibody (0.2 μg/mL) in an ELISA. (C) Representative SPR responses for binding of B7-2-Fc in twofold increments from 0.031 μM to immobilized SEB. (D) SEB and B7-2 interact directly as free molecules. Representative MST responses are shown for binding of labeled wt or tk2 SEB (240 nM) to increasing concentrations of B7-2-Fc or for binding of wt SEB to IgG Fc (error bars, SEM; n = 3). (E) Binding of SEB to cell-surface B7-2. HEK 293T cells were transfected to express B7-2 or with empty vector (EV) and after 36 h incubated for 1 h with recombinant wt or tk2 mutant SEB (μg/mL). Cells were washed three times with cold PBS before lysis. Western blots of equal amounts of total cell protein (Bradford assay) with 0.1 μg/mL αSEB antibody followed by 0.2 μg/mL horseradish peroxidase-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG (Top) or with 0.1 μg/mL αB7-2 antibody followed by 0.2 μg/mL horseradish peroxidase-conjugated donkey anti-goat IgG (Bottom); autoradiograms are from representative experiments. On the Right, both tk2 and wt recombinant SEB (μg/mL) were detected by Western blot with the αSEB antibody.