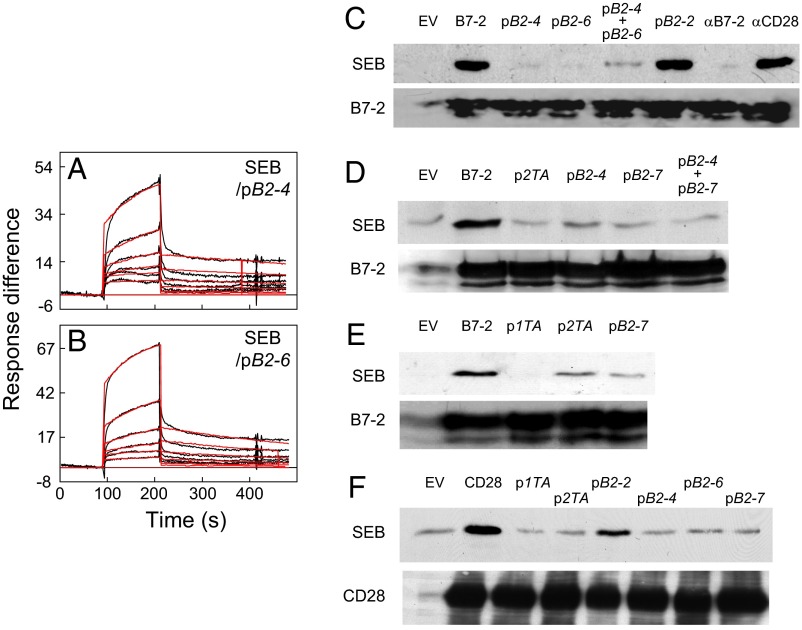
Fig. 5.
Peptide mimetics of the B7-2 dimer interface bind SEB and block binding of SEB to cell-surface B7-2 and CD28. (A and B) Representative SPR responses for binding of SEB in twofold increments from 0.78 μM to immobilized pB2-4 (A) and pB2-6 (B); graphical fits to the binding curves are presented in red; kinetic parameters show the specificity of these interactions (Table S1). (C–E) Peptide mimetics of the B7-2 or CD28 homodimer interface inhibit binding of SEB to cell-surface B7-2. HEK 293T cells were transfected to express B7-2 or with empty vector (EV) and after 36 h incubated for 1 h without addition (B7-2) or as indicated, with 5 μg/mL αB7-2 antibody, αCD28 monoclonal antibody (12), or 10 μg/mL B7-2 mimetic peptides pB2-2, pB2-4, pB2-6, or pB2-7, or CD28 mimetic peptides p1TA or p2TA (12) before further incubation for 1 h with 15 μg/mL recombinant wt SEB. Cells were washed three times with cold PBS before lysis. Western blots of equal amounts of total cell protein with αSEB antibody (Top) or αB7-2 antibody (Bottom) were done as for Fig. 2E; autoradiograms are from representative experiments. (F) Peptide mimetics of the B7-2 or CD28 homodimer interface inhibit binding of SEB to cell-surface CD28. HEK 293T cells were transfected to express CD28 (12) or with empty vector before incubation with peptides and SEB as above. Western blots show binding of SEB to CD28 (12) (Top) and expression of CD28, assayed with 0.1 μg/mL αCD28 antibody (Bottom).