Figure 1.
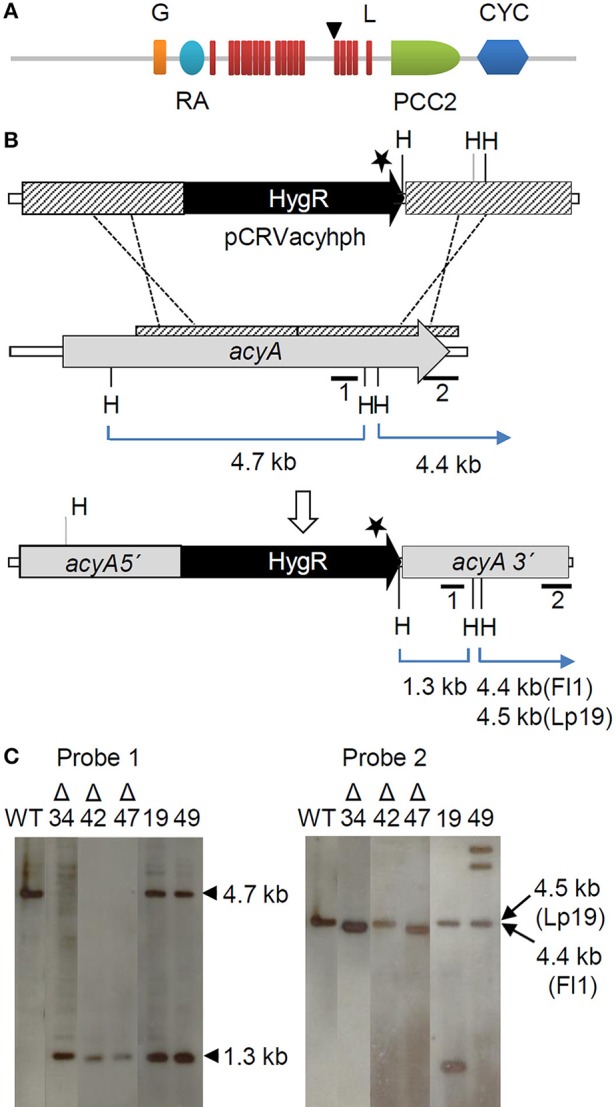
Disruption of acyA in E. festucae Fl1. (A) Domain architecture of AcyA in relation to the insertion site of the hygromycin resistance cassette (HygR). The protein contains the domains for G-alpha binding (G), ras association (RA), leucine rich repeats (L), protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C), and catalytic cyclic nucleotide biosynthesis (CYC) (Baker and Kelly, 2004). The HygR cassette was inserted (arrow) upstream of the phosphatase 2C (PPC2) and catalytic (CyC) domains. (B) Diagram of the acyA disruption locus in E. festucae Fl1. In vector pCRVacyhph, the HygR cassette is flanked by approximately 3 kb of DNA from the partial acyA gene (hatched) cloned from E. festucae var. lolii Lp19 (KR815911). The stop codon in the hygromycin resistance gene is indicated (⋆). The regions of homology between the Lp19 flanking regions and the corresponding Fl1 acyA sequence (hatched) is shown immediately above the Fl1 acyA gene, gene model Fl1M3.048730 (http://www.endophyte.uky.edu). Probes 1 and 2 (solid bars) were used in Southern-blot hybridization experiments (C) to confirm that the endogenous acyA gene had been disrupted and to ascertain the number of acyA copies in each strain respectively. (C) Southern-blot hybridization to confirm acyA insertion mutants. Genomic DNA was isolated from the wild-type (WT) plus a number of putative insertional mutants, and digested with HindIII. Probe 1 bound to the predicted 4.7 kb fragment in the wild-type acyA also in ectopic integrants acyA19 and acyA49 and to the 1.3 kb HindIII fragment of the disrupted acyA gene in ectopic integrants acyA19 & acyA49 and insertional mutants ΔacyA34 (Δ34), ΔacyA42 (Δ42) and ΔacyA47 (Δ47). Probe 2 was used to determine copy number, and bound to either a 4.4 kb or 4.5 kb HindIII fragment depending on whether the recombination locus was before or after the 66 bp indel in the Lp19 acyA.
