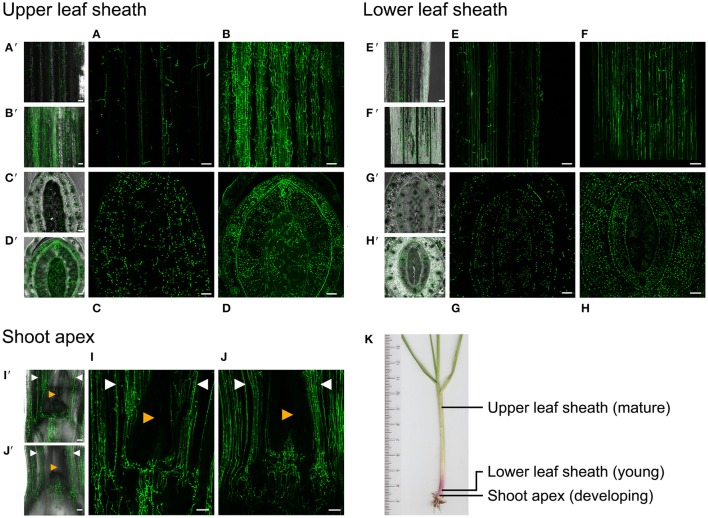
Figure 6.
Disruption of E. festucae acyA deregulates hyphal branching during host colonization. (A–J). Confocal laser scanning micrographs (CLSM) of E. festucae hyphae at three stages of host development. L. perenne leaves infected with the wild-type and disruption mutant ΔacyA42 are shown. Both strains are transformed with plasmid pTEFEGFP and constitutively express EGFP. (A′–J′), CSLM overlaid on corresponding phase contrast images of the same field of view. (K) L. perenne tiller showing the positions at which the tissue sections were taken. A/B, CLSM of a longitudinal section of the mature upper leaf sheath of the pseudostem 3.5 cm above the crown (base) of the tiller showing colonization by WT and ΔacyA42 hyphae respectively. (C,D) CLSM of a transverse section though the tiller at the same position as (A,B). The youngest developing leaf is in the center of the section and is enclosed by progressively older leaf sheaths. (E,F) CLSM of a longitudinal section of a young developing leaf sheath immediately above the crown of the tiller. (G,H) CLSM of a transverse section through the pseudostem at the same position as (E,F). (I,J) CSLM of a longitudinal section through the crown showing the position of hyphae relative to the shoot apex. The shoot apex (red arrow) is a small dome of overlapping leaf primordia visible only in the phase contract images (I′, J′). Hyphae are either not detectable in this tissue by confocal microscopy or are not present. Hyphae in the youngest leaves emerging from the shoot apex are marked by white arrows.