Fig. 2.
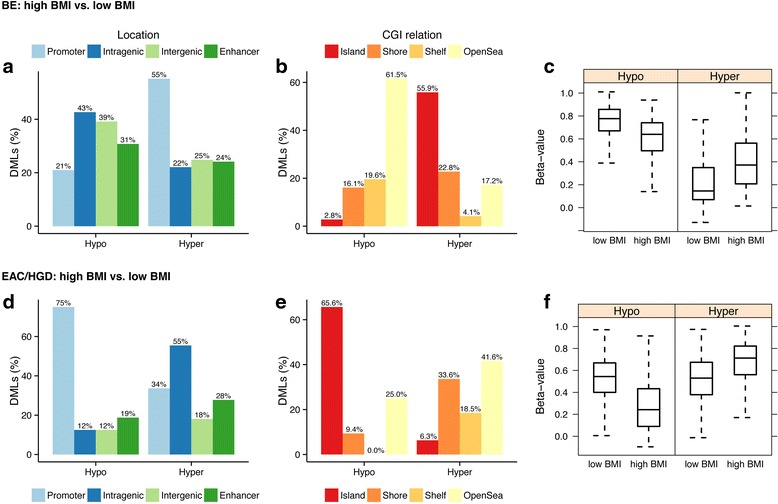
Genomic location, relationship to CpG islands, and methylation status of DML when comparing high vs. low BMI esophageal samples. In each panel, “Hypo” refers to percentage of DML that are hypomethylated in high BMI vs. low BMI samples; “Hyper” refers to percentage of DML that are hypermethylated in high BMI vs. low BMI samples. On the Y axis, DMLs (%) refers to the percentage of the total DML that are associated with a particular genomic location (a, d) or CGI relationship (b, e). Percentages may add up to more than 100 % because some probes were classified with more than one designation. Beta values are equivalent to percent methylation. a DML when comparing high BMI to low BMI BE cases by genomic region. Non-promoter regions were enriched with hypomethylated loci (p = 0.008), whereas promoter regions were borderline-enriched with hypermethylated loci (p = 0.06). b Location of DML when comparing high BMI to low BMI BE cases with respect to CpG island location. Non-CGI regions were enriched with hypomethylated loci (p = 8.4 × 10−8), whereas CpG island regions were enriched with hypermethylated loci (p = 0016). c Box and whisker plots showing distribution of DML that are hypomethylated in the high vs. low BMI BE cases (left) and hypermethylated in the high vs. low BMI BE cases (right). d DML when comparing high BMI to low BMI HGD/EAC cases by genomic region. Promoter regions were enriched with hypomethylated loci (p = 2.7 × 10−6). e Location of DML when comparing high BMI to low BMI HGD/EAC cases with respect to CpG island location. CpG island regions were enriched with hypomethylated loci (1.9 × 10−6), whereas non-island regions were enriched with hypermethylated loci (p = 6.5 × 10−5). f Box and whisker plots showing distribution of DML that are hypomethylated in the high vs. low BMI HGD/EAC cases (left) and hypermethylated in the high vs. low BMI HGD/EAC cases (right)
